Skip to content
Expanding Glacial Lakes in India
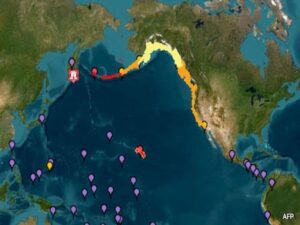
Kamchatka Earthquake & Tsunami (2025)
India’s Strategy for Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) Risks
State Assistance During Natural Disasters: Mechanisms and Funding
HIMALAYAN TRAGEDY – Impact and Control
FLOOD RISKS RISING IN HIGH MOUNTAIN ASIA
UTTARKASHI EARTHQUAKE SWARM
FOREST FIRES IN INDIA: A GROWING CRISIS
WAYANAD LANDSLIDES CATEGORIZED AS SEVERE DISASTER
Bhopal Gas Tragedy and Chemical Disasters in India
Disaster Management Act, 2005
Disaster Management Act (DM Act) of 2005