GEOGRAPHY
Poás Volcano
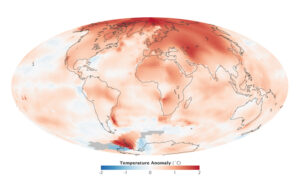
Arctic Amplification: 2024

Quantum Gravity Gradiometer (QGG)
Majuli River Island
Reclassification of Barytes, Felspar, Mica, and Quartz as Major Minerals
NODI BANDHAN SCHEME: A RIVER INTERLINKING INITIATIVE FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
OPPRESSIVE HEATWAVES

BRAHMAPUTRA RIVER SYSTEM

Rare Earth Elements (REEs)





