GS 1 – Geography
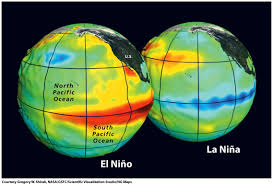
- ENSO is a recurring climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It involves interactions between the ocean and the atmosphere, leading to global weather fluctuations.
- Two main phases: El Niño (warming) and La Niña (cooling), along with a neutral phase.
Components
- El Niño
- Abnormal warming of central & eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Weakening of trade winds.
- Suppression of upwelling near South America.
- La Niña
- Abnormal cooling of central & eastern equatorial Pacific.
- Strengthening of trade winds.
- Enhanced upwelling near South America.
- Southern Oscillation
- Atmospheric component of ENSO.
- Refers to periodic shift in air pressure between Tahiti (French Polynesia) & Darwin (Australia).
- Measured using Southern Oscillation Index (SOI).
Global Impacts
- Alters global wind & rainfall patterns.
- Changes in jet streams, leading to extreme weather.
- Impacts monsoons, cyclones, droughts, floods.
ENSO & India
- El Niño → Weakening/Failure of Indian Summer Monsoon → Droughts (e.g., 2009).
- La Niña → Stronger monsoon → Excess rainfall & floods (e.g., 2010, 2020).
- Affects agriculture, food security, economy, water resources.
Monitoring & Prediction
- Monitored by NOAA, IMD, World Meteorological Organization.
- Indicators:
- Sea Surface Temperature (SST) anomalies.
- SOI values.
- Equatorial Pacific trade winds & convection patterns.




