A recent article in Nature spotlighted biofortified rice varieties developed by CAS, Beijing, under the headline ‘Gene-edited plants make the jump from farm to factory’.
Overview of Enzymes
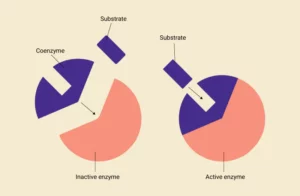
- Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions, playing a crucial role in boosting cellular metabolism efficiency.
- Many enzymes rely on helper molecules, known as cofactors, for their proper functioning. When these cofactors are organic molecules, they are referred to as coenzymes.
- Coenzymes bind to enzymes, aiding their activity, and are essential for a wide range of metabolic processes.
What is Coenzyme Q (Ubiquinone)?
- Coenzyme Q (CoQ), or ubiquinone, is an organic antioxidant with multiple isoprene units.
- It exists in ten different forms, ranging from CoQ1 to CoQ10, and is lipid-soluble, though insoluble in water.
- CoQ is critical for mitochondrial function and is found in every cell membrane, where it helps produce cellular energy.
Role of CoQ9 in Plants
- CoQ9, which contains nine isoprene units, is primarily found in cereal crops such as wheat, rice, oats, barley, corn, rye, and millet.
- It is also present in bamboo, barley, and flowering plants like cinnamon, avocado, and pepper.
Significance of CoQ10 in Human Health
- CoQ10 is a vital component of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, where it generates most of the body’s cellular energy.
- Organs with high energy demands, such as the heart, contain significant levels of CoQ10.
- While CoQ9 is available in common foods, humans require additional CoQ10 due to factors such as genetics, aging, and certain neurological disorders.




