Researchers at Kyoto University recently conducted a Phase I/II clinical trial to evaluate the safety and potential side effects of stem cell therapy using dopaminergic progenitors derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
About Parkinson’s Disease
- Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative condition characterized by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain.
- Dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter, plays a key role in regulating motor functions.
- While current treatments mainly consist of dopaminergic medications, these drugs do not address the loss of neurons and may cause long-term side effects.
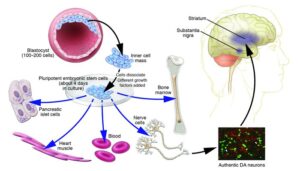
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- iPSCs are pluripotent stem cells generated from adult somatic cells such as skin or blood.
- These cells are reprogrammed back to an embryonic-like state, enabling them to differentiate into virtually any type of human cell.
- Applications of iPSCs include:
- Diabetes: Conversion into insulin-producing beta cells.
- Leukemia: Generation of new blood cells.
- Neurological Diseases: Potential treatment for conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
- iPSCs are useful in drug testing, disease modeling, and transplantation medicine.
Stem Cells
- Stem cells are unspecialized cells capable of developing into specialized cell types such as blood, muscle, or liver cells.
- Their ability to self-renew and differentiate makes them essential for regeneration and repair.
- Sources of stem cells include:
- Bone marrow
- Gastrointestinal tract (divides regularly)
- Organs like the pancreas or heart (divides only under certain conditions)
Comparison of Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells
| Feature | Embryonic Stem Cells | Adult Stem Cells |
| Potency | Pluripotent (can become any body cell) | Multipotent (can only become limited types of cells) |
| Source | Derived from embryos (blastocyst stage) | Found in mature tissues (e.g., bone marrow) |
| Growth in Lab | Can be easily cultured | Difficult to isolate and expand |
| Ethical Concerns | High | Low |




