GS I – Geography
Context
A recent study warns that the potential collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) could cause drastic drops in winter temperatures across northern Europe.
Cause of AMOC Disruption
Human-induced climate change, especially the accelerated melting of Greenland’s ice sheet, has introduced large volumes of freshwater into the North Atlantic. This influx reduces the salinity and density of seawater, which impairs the sinking process crucial to AMOC functioning.
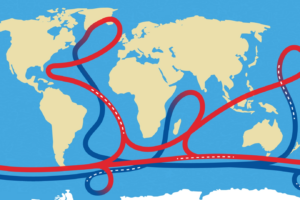
What is AMOC?
- Definition: AMOC is a large system of ocean currents that circulates water across the globe.
- Driving Mechanism: It is primarily driven by differences in water density, influenced by temperature and salinity.
- Role: It operates like a global conveyor belt, moving warm water from the tropics towards Greenland and returning cold water southward.
- Climate Tipping Point: AMOC is considered a potential climate tipping point—its collapse could cause sudden and irreversible changes in the global climate.
- Historical Context: A 2021 study revealed that AMOC is at its weakest in over 1,600 years.
Importance of AMOC
- Climate Regulation: Transports heat from the tropics to the North Atlantic, contributing to the mild climate of Europe.
- Carbon Cycle Contribution: Plays a significant role in absorbing and storing atmospheric CO₂, aiding in carbon regulation.
- Marine Nutrient Circulation: Facilitates the distribution of nutrients in oceans, sustaining ecosystems and global fisheries.
- Weather Influence: Influences major weather systems such as rainfall in West Africa and South America, and impacts Atlantic hurricane activity.
Impacts of AMOC Weakening
- Harsher European Winters: North-western Europe could experience extreme cooling and severe winters.
- Sea Ice Expansion: Diminished heat transfer may lead to substantial sea ice growth along north-western European coasts.
- Weakened Monsoon Systems: A disrupted AMOC may shift the Intertropical Convergence Zone southward, weakening monsoons in India, West Africa, and the Amazon.
- Accelerated Arctic Ice Melt: More ice melt from Greenland and the Arctic adds freshwater, further destabilizing AMOC.
- Increased Droughts: Regions like the Sahel in Africa may suffer severe droughts, threatening agriculture and livelihoods.
- Disrupted Marine Ecosystems: Changes in nutrient and heat flows can affect marine biodiversity.
- Regional Sea Level Rise: Particularly along the U.S. East Coast due to altered oceanic and atmospheric pressure systems.
- Reduced CO₂ Absorption: The ocean’s diminished carbon absorption capacity could aggravate global warming.




