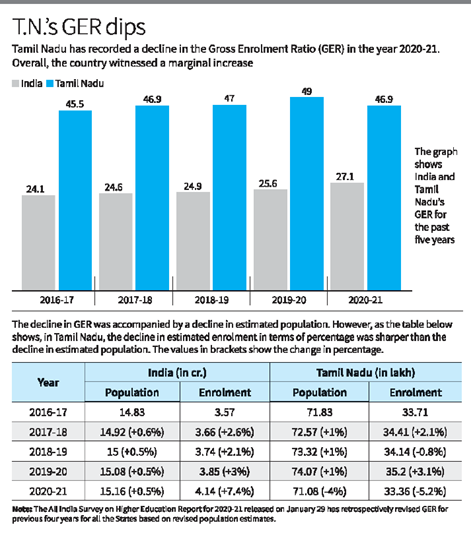
- Tamil Nadu’s Gross Enrolment Ratio dropped by 2.1 percentage points to 46.9% in 2020-21 from the year before, the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) released on Sunday showed.
- India recorded a marginal increase in GER from 25.6% to 27.3%.
- Tamil Nadu was among very few States that recorded a decline. This was the first time the State recorded a decline in the past five years.
- The data were based on the enrolment in the academic year 2020-21 when COVID-19 struck.
- Despite the decline, Tamil Nadu continued to have the highest GER among major States, followed by Uttarakhand (45.7%) and Kerala (43.2%). Chandigarh, Puducherry and Delhi have the highest of 66.1%, 60.8% and 47.6%, respectively.
Retrospective revision
- Interestingly, the report for 2020-21, released after a considerable delay, has retrospectively revised the GER for all the States for every year since 2016-17, based on the revised estimates of population for the 18-23 age group.
- (GER is calculated as a percentage of the total number of enrolments in higher education courses against the total projected population in the 18-23 age group).
- According to the report, GER was calculated until 2019-20 based on population projections made in the 2001 census. It has been revised in accordance with the 2011 census in 2020-21.
- Consequent to this revision, Tamil Nadu’s highly acclaimed GER of more than 50% in the year 2019-20 (51.4%) was revised to 49%, which further dropped to 46.9% in 2020-21.
- Only a few States — such as Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand and Punjab — recorded a decline in GER.
- The drop in GER in Tamil Nadu happened despite a decline in the population as per projected figures. This was because of a relatively sharper decline in the estimated enrolments.
Analysis by gender
- The drop in enrolments was more among male students than female students. The enrolment of male students dropped by 7%, while that of female students by 4%.
- The GER of male students consequently dropped from 48.1% in 2019-20 to 45.4% in 2020-21, while that of female students dropped from 49.9% to 48.6% in the same period.
- The drop was observed in almost all types of courses such as undergraduate, postgraduate, M. Phil, diploma and postgraduate diploma
- Only enrolments in Ph.D and courses classified as “Integrated”, which were small in number, recorded an increase.
- The drop in GER was witnessed for students from the Scheduled Castes too.
- Their GER, which was already significantly lower than the overall GER, dropped from 39% to 36.8%.
- The GER of the Scheduled Tribe students, who are smaller in number, increased from 40% to 40.6%.
GER improved in 2021-22 at primary, upper primary, and higher secondary levels of school education compared to 2020-21
- Ministry of Education released a detailed report on Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) 2021-22 on school education of India.
- The UDISE+ system of online data collection from the schools was developed by Department of School Education & Literacy in the year 2018-19 to overcome the issues related to erstwhile practice of manual data filling in paper format . In UDISE+ system, improvements have been made particularly in the areas related to data capture, data mapping and data verification.
- In UDISE+ 2021-22, additional data on important indicators viz., digital library, peer learning, hard spot identification, number of books available in school library, etc have been collected for the first time to align with the NEP 2020 initiatives.
Students and Teachers in School Education:
- In 2021-22 total students enrolled in school education from primary to higher secondary stood at 25.57 crore as compare to 25.38 crore enrolment in 2020-21, registering an increase of 19.36 lakh enrolments.
- Total number of Scheduled caste enrolment increased to 4.82 Crore in 2021-22 as compared to 4.78 Crore in 2020-21. Similarly, total Scheduled Tribe enrolment increased to 2.51 crore in 2021-22 from 2.49 crore in 2020-21. Total other backward students also increased to 11.48 crore in 2021-22 from 11.35 crore in 2020-21.
Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER)
- Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) which measures the general level of participation has improved in 2021-22 at primary, upper primary, and higher secondary levels of school education, as compared to 2020-21.
- Notably, GER in higher secondary has made significant improvement from 53.8% in 2021-21 to 57.6% in 2021-22.
- Total enrolment of Children with Special Needs (CWSN) in 2021-22 stands at 22.67 lakh as compared to 21.91 lakh in 2020-21 showing an improvement of 3.45% over 2020-21.
- 07 lakh teachers are engaged in school education during 2021-22 out of which more than 51% are female teachers.
- Further, in 2021-22, the Pupil Teacher Ratio (PTR) stood at 26 for primary, 19 for upper primary, 18 for secondary and 27 for higher secondary, showing an improvement since 2018-19. The PTR for primary, upper primary, secondary and higher secondary was 28, 19, 21, and 30 respectively during 2018-19.
- In 2021-22 over 12.29 crore girls are enrolled in primary to higher secondary showing an increase of 8.19 lakh compare to the enrolment of girls in 2020-21.
- The Gender Parity Index (GPI) of GER shows the representation of females in school education is in line with representation of girls in population of corresponding age group.
- The GPI value at all level of school education are one or more implying more participation of girls in the school education.
- In 2021-22, total number of Scheduled Caste (SC) students from Primary to Higher Secondary has gone up to 4.83 crore from 4.78 crore in 2020-21. Similarly, total Scheduled Tribe (ST) students have gone up from 2.49 crore to 2.51 crore and Other Backward Caste (OBC) students from 11.35 crore to 11.49 crore during 2020-21 and 2021-22.
- Total number of schools in 2021-22 stood at 14.89 lakhs as compared to 15.09 lakhs in 2020-21. The decline in total schools is mainly due to closure of private and other management schools and grouping/ clustering of schools by various States.
School Infrastructure: Impact of Samagra Shiksha scheme:
The availability of basic infrastructure facilities in schools as on 2021-22 are as follows:
- Electricity connection: 89.3%
- Drinking water: 98.2%
- Girls toilet: 97.5%
- CWSN toilet: 27%
- Handwash facility: 93.6%
- Playground: 77%
- Ramp with Handrail for CWSN: 49.7%
- Library/ Reading room/ Reading corner: 87.3%
- Sustainable Environment Initiatives for School
- Kitchen Garden: 27.7%
- Rain Water Harvesting: 21%
SOURCE: THE HINDU, THE ECONOMIC TIMES, PIB
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs



