Context:
India’s coal consumption has surpassed that of North America and Europe, highlighting the significant environmental impacts associated with its usage.
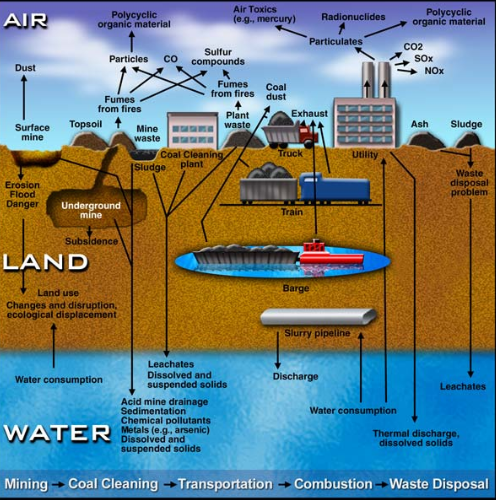
Coal Mining:
- Habitat Destruction and Contamination: Coal mining devastates natural habitats and pollutes the environment, affecting humans, animals, and plants. It leaves permanent scars on the landscape.
- Mine Wastes: Mining generates massive amounts of waste, including heavy metals that can seep into nearby water bodies such as rivers, streams, and groundwater.
- Acid Mine Drainage (AMD): This occurs when exposed coal interacts with water, creating sulfuric acid that dissolves toxic metals, leading to water contamination. This can harm aquatic life and make water unsuitable for human use.
- For example, in New Zealand, up to 125 km of waterways on the West Coast of the South Island are polluted by both historical and current coal mines.
- Health and Safety Risks: Coal mining poses severe health risks, including respiratory diseases like emphysema and black lung disease, exposure to toxic gases, noise-induced hearing loss, and heat-related illnesses.
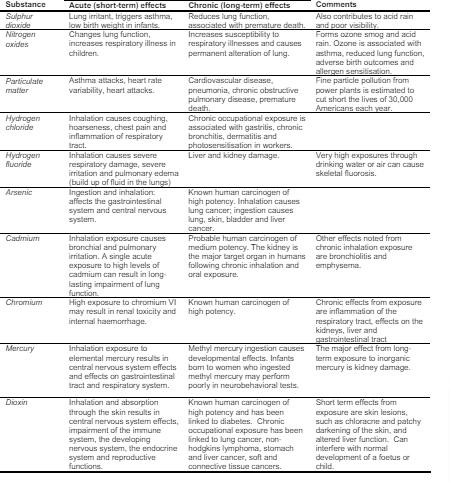
Health Effects of Coal-Fired Power Plant Pollutants:
- Hazardous Air Pollutants: Coal-fired power plants release over 60 hazardous air pollutants through various pathways:
- Fly ash expelled from smokestacks.
- Bottom ash left after coal combustion.
- Waste gases from scrubber units designed to remove specific pollutants.
- Gases emitted directly into the atmosphere.
Transportation:
- The transportation of coal by trucks, railroads, and barges adversely affects air and water quality.
Coal Usage in India:
- In 2023, India consumed more coal than North America and Europe combined, according to a report by the Energy Institute and KPMG titled ‘2024 Statistical Review of World Energy’.
- Coal meets 55% of India’s energy needs, predominantly used in power generation and industrial processes.
- The top five Indian states with the highest coal reserves are Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh.
India’s Renewable Energy Commitments:
- As a signatory to the Paris Agreement, India has pledged to reduce its carbon intensity and increase the share of non-fossil fuel-based electricity to 40% by 2030.
- India has set ambitious renewable energy targets, including a pledge at COP26 to achieve 500 GW of renewable energy by 2050.
- India co-founded the International Solar Alliance to promote the global deployment of solar energy, particularly in sun-rich countries.
- Initiatives have been launched to promote green hydrogen production and adoption as part of India’s clean energy strategy.
- The National Action Plan on Climate Change outlines measures and strategies to promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable development.





