GS 3 – SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context:
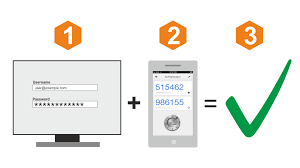
As cyber threats increase, relying solely on passwords has become inadequate for protecting online accounts. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring two different factors to verify a user’s identity.
Key Highlights
- What is 2FA?
- 2FA uses two independent factors to verify a person’s identity:
- Something you know – e.g., password or PIN.
- Something you have – e.g., a code sent to your phone or an authenticator app.
- Even if a hacker obtains the password, they cannot access the account without the second factor.
Example:
Logging into your bank account requires both a password and a one-time password (OTP) sent via SMS or app.
- Why Passwords Alone Are Insecure
- Users often:
- Reuse passwords across platforms.
- Use weak or predictable passwords.
- Hackers exploit this using:
- Phishing attacks to trick users into sharing passwords.
- Data breaches to steal passwords from databases.
- How 2FA Improves Security
- Adds a dynamic code generated in real time.
- Even if the static password is stolen, hackers cannot log in without the second factor.
- Prevents account takeover, especially in banking, emails, and government services.
- Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP)
- A common form of 2FA uses Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP).
- The app (e.g., Google Authenticator) and the server both:
- Use the same secret key and current time to generate a temporary code, valid for about 30 seconds.
- Codes expire automatically, reducing misuse risk.
Process Flow:
- You log in with your username and password.
- The app generates a six-digit code synced with the server’s clock.
- You enter the code for verification.
- If the code matches, access is granted.
- Security Mechanism – Hash Functions
- Hash function: Converts input data into a fixed-length string of characters.
- Ensures that:
- Passwords and codes are stored securely.
- Original data cannot be reverse-engineered easily.
- Common algorithms:
- SHA-1, SHA-256, etc.
These hashes are fundamental to generating secure OTPs.
Benefits of 2FA:
- Protects against phishing attacks and credential theft.
- Adds multi-layer defense beyond just passwords.
- Essential for:
- Banking apps
- Email security
- Government e-services like Aadhaar and GST portals
Challenges:
- User inconvenience: Slightly longer login process.
- Dependency on devices: If the phone is lost, access recovery can be difficult.
- Time synchronization issues: Server and device clocks must match.




