- A lot rides on lithium in the age of electric mobility and personal devices.
- But the lightest metal known to humans is also famously scarce.
- Hence, the discovery of lithium deposits in J&K could come as a potential game changer for India. Chethan Kumar breaks it down.
Lithium
- Referred to as “white gold” – Lithium metal is soft, white, and lustrous—and several of its alloys and compounds are produced on an industrial scale.
- Lithium is a non-ferrous metal and is one of the key components in EV batteries.
Appearance
- A soft, silvery metal.
- It has the lowest density of all metals.
- It reacts vigorously with water.
Uses
- Electronics:The most important use of lithium is in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras and electric vehicles.
- Glass and Grease:Lithium-ion batteries are also used in ceramics and glass, lubricating greases, polymer production, and air treatment.
- Medical:Lithium is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for things like heart pacemakers, toys and clocks. It is also used in psychiatric medications and in dental imprints. Lithium carbonate is used in drugs to treat manic depression.
- Nuclear Weapons:The lighter of the two lithium isotopes is used in the production of Tritium, a key component of nuclear weapons.
- Infrastructure:Lithium metal is made into alloys with aluminum and magnesium, improving their strength and making them lighter. Aluminum-lithium alloys are used in aircraft, bicycle frames and high-speed trains.
- Fuel:Lithium hydride is used as a means of storing hydrogen for use as a fuel.
- Other:A magnesium-lithium alloy is used for armour plating. Lithium chloride is one of the most hygroscopic materials known, and is used in air conditioning and industrial drying systems (as is lithium bromide). Lithium stearate is used as an all-purpose and high-temperature lubricant.
Biological role
- Lithium has no known biological role. It is toxic, except in very small doses.
Natural abundance
- Lithium does not occur as the metal in nature,but is found combined in small amounts in nearly all igneous rocks and in the waters of many mineral springs.
- Spodumene, petalite, lepidolite, and amblygonite are the more important minerals containing lithium.
- Most lithium is currently produced in Chile, from brines that yield lithium carbonate when treated with sodium carbonate.
- The metal is produced by the electrolysis of molten lithium chloride and potassium chloride.
Lithium Production in the world
- Australia, Chile, China and Argentina are the world’s top four lithium-producing countries.
Lithium Triangle
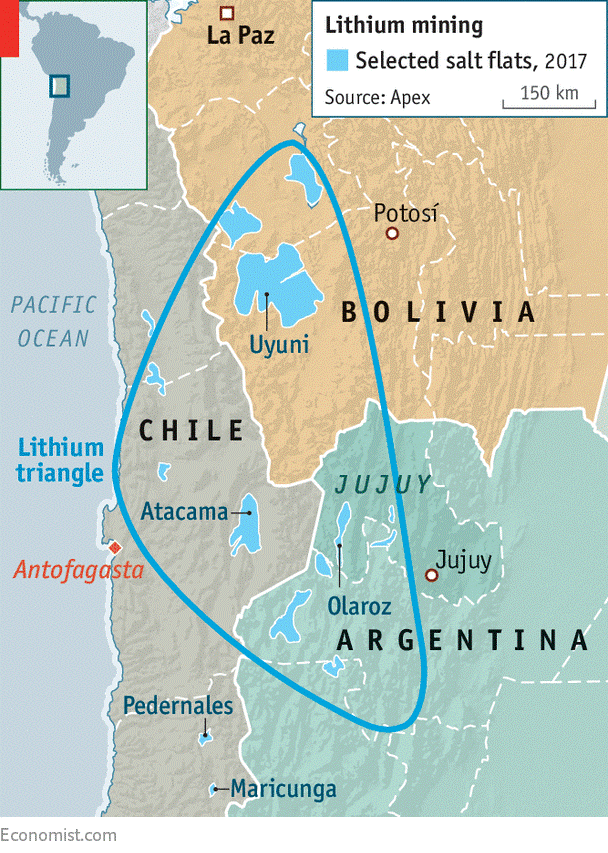
- The Lithium Triangle is a region of the Andes rich in lithium reserves around the borders of Argentina, Bolivia and Chile.
- The lithium in the triangle is concentrated in various salt pans that exist along the Atacama Desert and neighboring arid areas.
- The area is thought to hold around 54% of the world’s lithium reserves.
The Indian Navy has shown interest in the Lithium Triangle as lithium will be required on Li-ION batteries that are planned to be fitted in future submarines.
Potential Geological domains of Lithium in India
- Brines of Sambhar and Pachpadra in Rajasthan, and Rann of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- The major mica belts in Rajasthan, Bihar, and Andhra Pradesh, and the pegmatite belts in Odisha and Chhattisgarh apart from Karnataka, are the other potential geological domains.
Mapping reserves
- Experts say while India requires lithium for its energy needs, there has been no comprehensive effort to map local reserves of lithium so far.
- India is seen as a late mover in attempts to enter the lithium value chain.
- The discovery is coming at a time when EVs are predicted to be a sector ripe for disruption.
- There can be an inflection point for battery technology – with several potential improvements to the li-ion technology, and alternatives are in advanced stages of commercialization.
SOURCE: THE HINDU, THE ECONOMIC TIMES, PIB
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs

