GS3 – Environment
Context:
UN negotiations in Geneva failed to reach consensus on a global plastic treaty, with disagreements over including health risks alongside waste management.
Why Plastic is a Concern
- Origin: Made from fossil fuel–based polymers, valued for being cheap and versatile.
- Chemicals: Over 16,000 chemicals may be present in plastics; more than 4,000 are hazardous, especially in PVC, PET, and polyurethane.
- Data Gaps: Limited scientific understanding of their long-term health impacts.
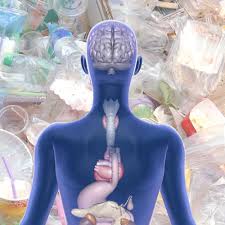
Health Implications
- Exposure Sources: Packaging, toys, cosmetics, paints, electronics, and medical devices.
- Toxic Substances: Bisphenols, phthalates, PFAS, PBDEs, PCBs.
- Associated Health Risks: Thyroid disorders, hypertension, cancers, gestational diabetes.
- Microplastics: Detected in blood, breast milk, placenta, and bone marrow; possible but unconfirmed links to multiple illnesses.
India’s Stance & Policies
- Bans: Single-use plastics prohibited in ~20 States (targeting low-reusability, non-recyclable items).
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Assigns responsibility to companies but suffers from weak implementation.
- Approach: Treats plastics mainly as a waste disposal issue, not as a public health hazard.




