GS3- ENVIRONMENT
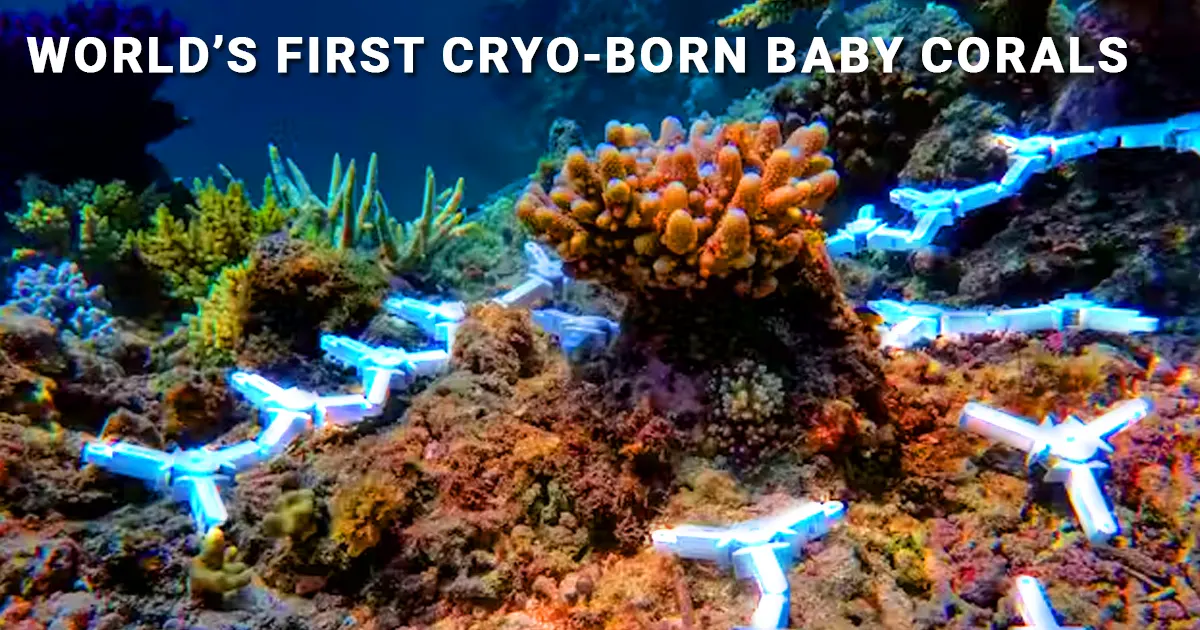
This groundbreaking achievement in coral conservation and restoration represents a significant step toward mitigating the impacts of climate change on coral ecosystems. Australian researchers have pioneered this technique to restore damaged reefs.
About Cryo-Born Corals
Cryo-Born Corals: Created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at ultra-low temperatures to preserve them for future use.
Cryopreservation Process
- Challenges: Coral cells contain water, which can form harmful ice crystals when frozen.
- Solution: Cryoprotectants are used to remove water from cells and protect cell structures during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience:
- Millions of heat-tolerant corals will be introduced annually to reefs to combat warming ocean temperatures.
- Selective Breeding Advantages:
- Overcomes the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year.
- Enables selective breeding and repeated use of colonies for reproduction.
About Coral Reefs
- Definition: Corals are invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria. They form reefs through colonies of polyps that secrete limestone skeletons.
- Symbiosis: Depend on zooxanthellae (symbiotic algae) for nutrients through photosynthesis.
- Distribution: Found in shallow, sunlit waters (30°N to 30°S latitude) with temperatures of 16–32°C.
- Depth: Typically grow at depths less than 50 meters where light is sufficient.
Threats to Coral Reefs
- Climate Change:
- Ocean warming leads to coral bleaching.
- Ocean acidification weakens coral skeletons.
- Pollution:
- Runoff containing chemicals and sediments smothers corals.
- Overfishing:
- Disrupts reef ecosystems by removing key species.
- Destructive Practices:
- Practices like blast fishing and coral mining destroy reef habitats.
- Diseases:
- Coral diseases are becoming more prevalent due to stress from warming oceans.
Global Initiatives for Coral Conservation
- Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI): Focuses on marine biodiversity conservation in Southeast Asia.
- International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI): Promotes coral reef protection globally.
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 14): Emphasizes conserving marine ecosystems.
India’s Efforts to Conserve Coral Reefs
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
- Examples: Gulf of Mannar, Lakshadweep, and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Coral Rehabilitation Projects:
- Initiatives like coral transplantation and artificial reef deployment.
- Legislative Measures:
- Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) norms to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Mangrove and Coral Reef Conservation:
- Schemes like Mangroves for the Future (MFF) address coastal and marine biodiversity.
- Research and Monitoring:
- Institutions like the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR) and Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) actively study and monitor coral reefs.




