GS 3
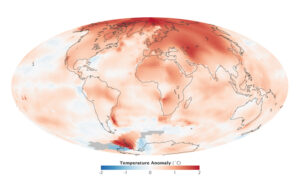
According to the latest European State of the Climate Report for 2024, Europe is experiencing warming at nearly twice the pace of the global average. This accelerated heating trend is triggering widespread environmental and climatic shifts.
What Is Arctic Amplification?
Arctic amplification refers to the intensified warming seen in Polar Regions—particularly in the Arctic—compared to the global average temperature rise. It is a specific case of a broader effect known as polar amplification, where atmospheric changes result in disproportionately high temperature increases near the Earth’s poles.
This process is assessed relative to the average rise in global temperatures and is most pronounced in the Arctic. The primary cause is an imbalance in the Earth’s radiation budget, driven largely by the buildup of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, which trap additional heat in the atmosphere.
Several key mechanisms contribute to Arctic amplification:
- Ice-Albedo Feedback: Melting sea ice reveals darker ocean or land surfaces that absorb more sunlight, causing further warming.
- Lapse Rate Feedback: Warming alters the rate at which temperature decreases with altitude, especially in cold regions.
- Water Vapor Feedback: Warmer air holds more moisture, which itself is a greenhouse gas, further intensifying warming.
- Ocean Heat Transport: Changes in ocean currents carry more heat to polar areas, amplifying regional temperature increases.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
The Arctic is currently heating at a rate three to four times greater than the global average—a stark example of Arctic amplification in action. As sea ice melts, reflective surfaces are replaced by darker ones, such as open water, which absorb more solar energy and increase warming even more.
Temperature Trends: Europe vs. Global Averages
- Since the pre-industrial period (1850–1900), global temperatures have risen by around 1.3°C.
- In 2024, the world temporarily exceeded the 1.5°C warming threshold.
- Europe, however, has seen an average temperature rise of about 2.4°C, marking it as one of the most rapidly warming continents.
This heightened warming has triggered a series of extreme weather phenomena across Europe, including:
- Record-breaking heatwaves
- Intense rainfall
- Frequent flooding events
Regional Variations Across Europe
- Eastern Europe saw warmer and sunnier conditions throughout the year.
- Western Europe experienced a shift toward more overcast and wetter weather.
- Southeastern Europe—including countries like Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, and Croatia—faced their longest heatwave on record in 2024.
Additionally, the number of days classified as “cold stress days” hit an all-time low, and instances of below-freezing temperatures declined significantly.




