GS3 ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
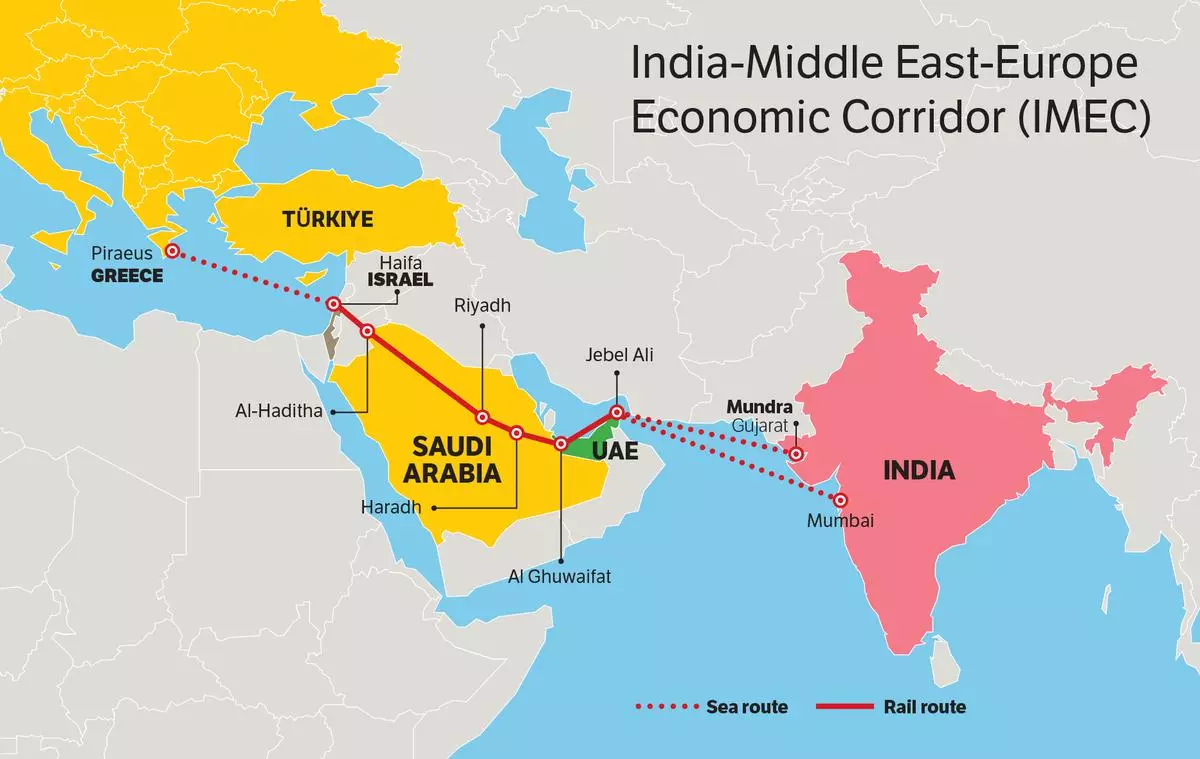
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) is gaining momentum with recent initiatives from RITES to improve trade and connectivity between India, the Middle East, and Europe. RITES is focusing on creating a digital interface for cargo clearance between Indian and Middle Eastern ports, marking the first phase of a virtual trade corridor.
Digital Interface Connectivity Project
- RITES is developing software to streamline cargo clearances and improve export-import procedures.
- The project will integrate IT systems and logistics support to simplify documentation and clearances at ports.
Interlinking Payment Systems
- India and the UAE have agreed to link their payment platforms, integrating UPI (India) with AANI (UAE).
- The interlinking of RuPay and JAYWAN debit/credit cards will enhance financial cooperation between the two countries.
What is IMEC?
- A 4,800 km trade and transport corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Announced in September 2023, it includes ship-to-rail networks and road transport routes.
- Strategically seen as an alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- It features two corridors:
- East Corridor: Links India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Connects the Gulf to Europe.
- Infrastructure includes an electricity cable, hydrogen pipeline, and high-speed data cable.
- Key signatories: India, USA, Saudi Arabia, UAE, European Union, Italy, France, Germany.
Key Ports Connected
- India: Mundra, Kandla, JNPT.
- Middle East: UAE (Fujairah, Jebel Ali, Abu Dhabi), Saudi Arabia (Dammam, Ras Al Khair).
- Israel: Haifa Port (via Saudi Arabia and Jordan).
- Europe: Greece (Piraeus), Italy (Messina), France (Marseille).
Objectives of IMEC
- Establish an efficient transport network between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Lower costs, improve trade efficiency, and reduce GHG emissions.
- Strengthen economic ties and create employment opportunities.
Geopolitical and Economic Implications
Geopolitical Impact
- Counter China’s BRI, offering an alternative trade route.
- Strengthens international ties between Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Bypasses Pakistan’s blockade, improving India’s connectivity to the West.
- Enhances India’s political and economic relationships with the Gulf nations.
- Promotes regional peace and stability.
- Expands potential to connect to Africa for broader infrastructure development.
Economic Impact
- Boosts trade, reducing India-Europe trade routes by 40% compared to the Suez Canal.
- Promotes industrial growth and generates jobs in infrastructure, trade, and logistics.
- Strengthens energy security by ensuring stable access to resources from the Middle East.
- Facilitates the development of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) along the route, attracting foreign investment.
Challenges Facing IMEC
- Logistics and connectivity issues due to multiple countries and systems involved.
- Missing rail links, especially in the Middle East.
- Challenges in coordination among countries with differing legal systems.
- Competition from existing routes, especially the Suez Canal.
- High development costs, estimated between $3 billion to $8 billion.
Infrastructure Development
- RITES is working on bridging infrastructure gaps to connect West Coast ports to the Dedicated Freight Corridor, including the Vadhavan Port, aiming to enhance logistics.
Overseas Expansion and Export Growth
- RITES is exploring Middle East consultancy projects and focusing on rolling stock exports to Latin America and Bangladesh, bidding for projects independently of Line of Credit options.
[box]
UPSC Mains Question:
“Discuss the geopolitical and economic implications of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC). How does it serve as a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and what are the key challenges faced in its development?”
[button color=”purple ” size=”medium” link=”https://forms.gle/Wzz7M6oVE4bQS8Ws8″ icon=”” target=”true”]Upload Answer[/button]
[/box]




