G3 3 – ENVIRONMENT – SPECIES
Context: China’s Ambassador to India, Xu Feihong, highlighted the historical significance of the Tea Horse Road, emphasizing its role in India-China trade via Tibet.
What is the Tea Horse Road?
- Also known as Chamadao, it was an ancient trade route linking China, Tibet, and India.
- Served as a major commercial corridor for trading Chinese tea in exchange for Tibetan horses.
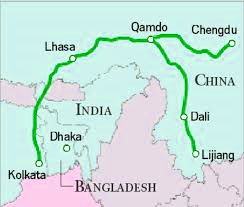
Route and Regional Connections
- Origin: Southwest China (Yunnan & Sichuan).
- Pathway: Passed through Tibet, Nepal, and India.
- Destination: Reached Kolkata, from where tea was exported to Europe and other Asian markets.
Trade Mechanism
- Major Exports:
- China: Tea, textiles, rice noodles, and sugar.
- Tibet: Horses, gold, saffron, leather, and medicinal herbs.
- Caravan System: Pack animals like yaks, mules, and horses were used for transportation.
- Challenging Terrain: Traders navigated 10,000-foot-high mountains, harsh climates, and bandit attacks.
- Tea Packaging: Tea was compressed into bricks for easy transport and even used as currency in Tibet.
- Lijiang (Old Town): A major distribution hub where the Silk Road in the south merged with the Ancient Tea Horse Road.
Dynastic and Historical Importance
- Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE): The first recorded trade between China and Tibet via this route.
- Song Dynasty (960-1279 CE): Established official tea-for-horses trade markets at border regions.
- Ming & Qing Dynasties (1368-1912 CE): Expanded the route into a regulated trade network, controlling tea exports and military horse imports.
- 20th Century: Used during World War II for supply transport but declined after Mao Zedong’s land reforms (1949).
Significance of the Tea Horse Road
- Economic Exchange: Strengthened trade and commercial ties between India, Tibet, and China.
- Military Strength: Helped supply Tibetan war horses for China’s military.
- Cultural Impact: Facilitated the spread of Buddhism, medicinal herbs, and textiles across the Himalayas.
- Heritage & Tourism: Parts of the route are being preserved as UNESCO heritage sites and promoted for historical tourism.




