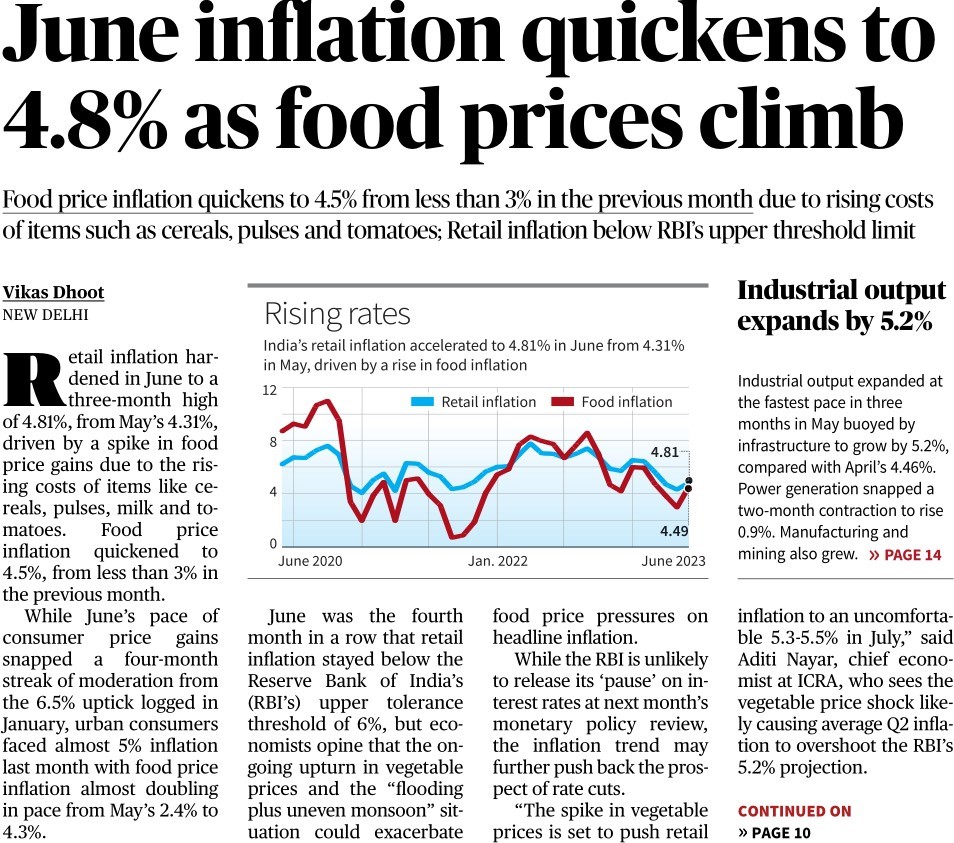
Retail inflation hardened in June to a three-month high of 4.81%, from May’s 4.31%, driven by a spike in food price gains due to the rising costs of items like cereals, pulses, milk and tomatoes. Food price inflation quickened to 4.5%, from less than 3% in the previous month.
June was the fourth month in a row that retail inflation stayed below the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI’s) upper tolerance threshold of 6%, but economists opine that the ongoing upturn in vegetable prices and the “flooding plus uneven monsoon” situation could exacerbate food price pressures on headline inflation.
RETAIL INFLATION
Retail inflation refers to the measure of the overall increase in the average price level of goods and services purchased by consumers over a specific period of time. It is also known as consumer price inflation (CPI). Retail inflation is typically calculated by tracking the price changes of a basket of goods and services commonly consumed by households.
The rate of retail inflation is commonly expressed as a percentage and is used as an important economic indicator to gauge changes in the cost of living and the purchasing power of consumers. RBI closely monitor retail inflation as it has significant implications for monetary policy decisions, wage negotiations, and economic forecasting.
Several factors can contribute to changes in retail inflation, including: Demand and supply dynamics:
When demand for goods and services exceeds supply, prices tend to rise, leading to inflation. Conversely, if supply outpaces demand, prices may decrease, leading to deflation.
Cost of production:
Increases in input costs, such as raw materials, labour, or energy, can lead to higher production costs, which may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Monetary policy:
Central banks play a crucial role in managing inflation through their monetary policy tools. Adjustments in interest rates and money supply can influence inflationary pressures in an economy.
Exchange rates:
Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the prices of imported goods and commodities, which, in turn, affect retail inflation.
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs



