
A strategy known as “Climate-Smart Agriculture” (CSA) aids in directing efforts to change agri-food systems towards environmentally friendly and climate-resilient methods. CSA is in favour of achieving globally recognised objectives like the SDGs and the Paris Agreement.
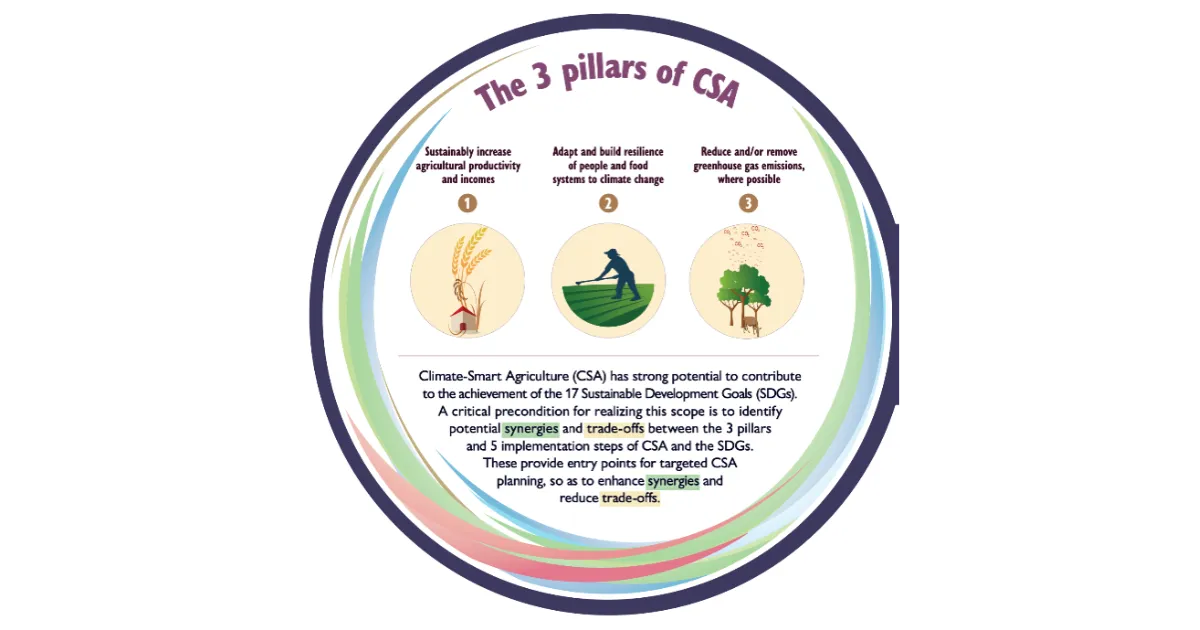
The three main objectives of CSA
- Sustainably increase agricultural productivity and incomes: This can be achieved through a variety of practices, such as using improved crop varieties, adopting sustainable soil management practices, and investing in irrigation infrastructure.
- Adapt and build resilience to climate change: This involves developing strategies to cope with the impacts of climate change, such as drought, heat stress, and flooding. This can be done through practices such as diversifying crop varieties, using water-efficient irrigation systems, and developing early warning systems for extreme weather events.
- Reduce/remove greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions: Agriculture is a major source of GHG emissions, so it is important to find ways to reduce these emissions. This can be done through practices such as using cover crops, adopting conservation tillage, and improving livestock manure management.
The Four Betters
- Better production
- Better nutrition
- Better environment
- Better life for everyone
These are the cornerstones of the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031, which is endorsed by CSA. The definition of a CSA practise varies based on the socioeconomic, environmental, and climate change conditions of the local area.
Five action points are suggested by FAO to implement the approach:
- Increasing the body of evidence supporting CSA
- Bolstering national and local institutions
- Supporting enabling policy frameworks
- Improving funding and financing options
- Putting CSA practises into practise at the field level
Policies and planning
It is necessary to integrate climate-smart agriculture into all major government spending, policy, and planning frameworks. For CSA policies to be successful, they must support the objectives of sustainable development, poverty alleviation, and wider economic growth. They must also be incorporated into social safety net initiatives, disaster risk reduction plans, and activities.
In order to create an enabling policy environment, it is imperative that different sectors addressing climate change, agricultural development, and food security at the national, regional, and local levels coordinate and integrate.
Farmers are encouraged to adopt climate-smart practises and get past initial investment barriers by offering incentives for adopting CSA, such as payments for environmental services (managing land to provide an ecological service).
Climate-smart agriculture in India
India is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change, and its agricultural sector is already being affected by the impacts of climate change. As a result, the Indian government has made a commitment to promoting CSA. The government has launched a number of initiatives to support CSA, including the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) and the National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) project.
CSA has the potential to make a significant contribution to India’s food security and climate change goals. However, there are a number of challenges that need to be addressed in order to scale up CSA in India.
Challenges
- Lack of awareness and understanding of CSA: Many farmers are not aware of CSA or its potential benefits.
- Limited access to CSA technologies and practices: Many farmers do not have access to the technologies and practices that they need to implement CSA.
- Inadequate financial support for CSA: There is not enough financial support available to farmers to adopt CSA practices.
Despite these challenges, there is a growing movement in India to promote CSA. The government, NGOs, and farmers are all working together to raise awareness of CSA, develop new technologies and practices, and make CSA more affordable for farmers.
Some examples of CSA practices in India
- Crop diversification: Farmers are planting a wider variety of crops to reduce their risk of crop failure due to climate change.
- Water-efficient irrigation systems: Farmers are using drip irrigation and other water-efficient irrigation systems to conserve water.
- Cover crops: Farmers are planting cover crops to protect the soil from erosion and improve soil fertility.
- Conservation tillage: Farmers are using conservation tillage practices to reduce soil erosion and improve soil health.
- Improved livestock manure management: Farmers are using improved manure management practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
CSA is an important tool for ensuring food security and climate resilience in India. By promoting CSA, India can make its agricultural sector more sustainable and productive, and help to feed its growing population.
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
