Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code is an important law made by the Parliament of India in recent years in order to harmonize India’s scattered and divergent bankruptcy laws. The enactment of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code was important to reduce the pilled-up non-performing assets of the banks and protracted resolution of the debts. The President of India gave assent in May 2016.
The process followed under the IBC
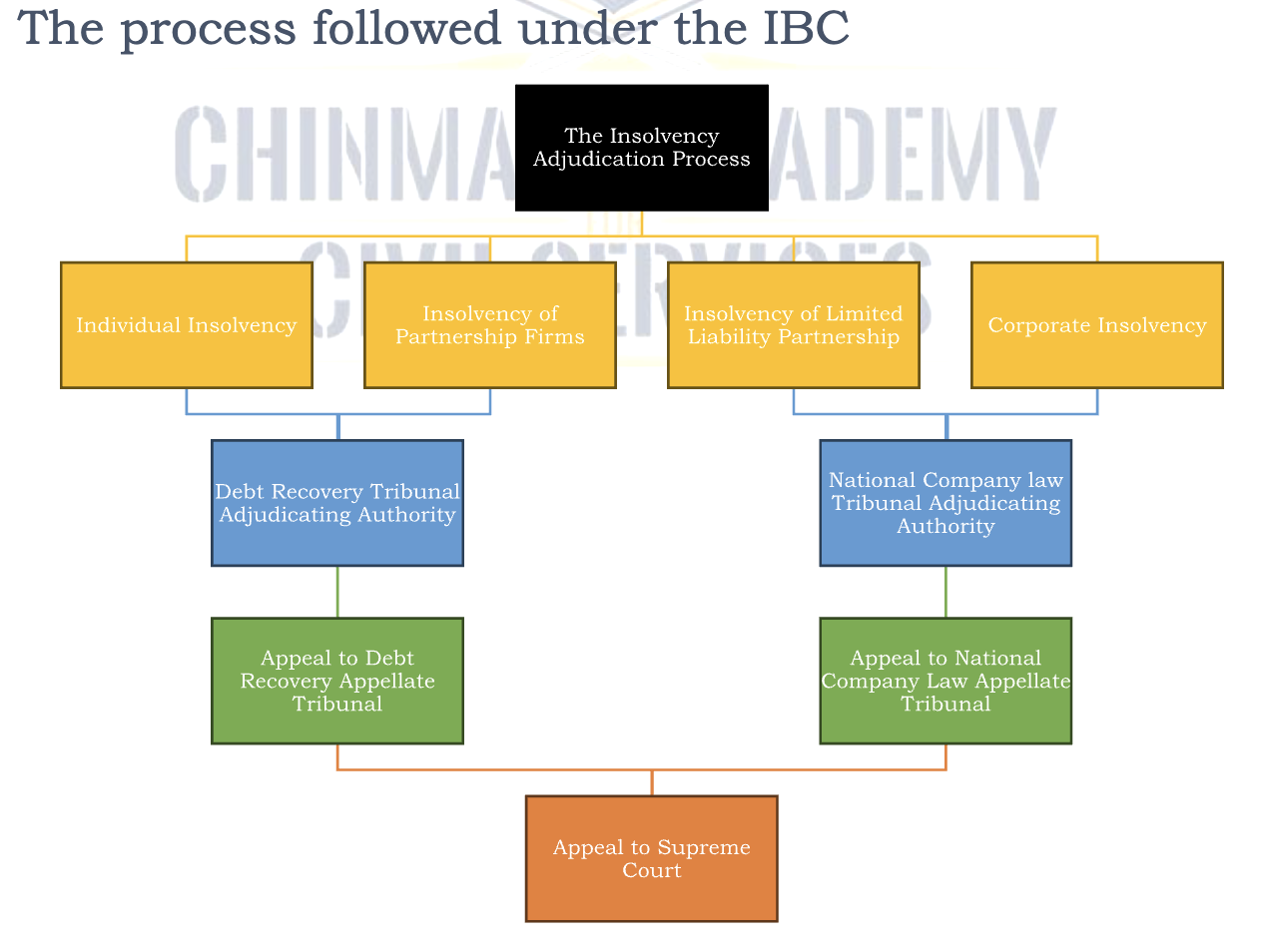
Benefits
As a result of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, the average time taken to resolve a bankruptcy has decreased.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code assist India in doing business and obtaining credit easier.
- Its rank of India in getting credit has improved from 62 in 2017 to 25 in 2020;
- India’s rank in ease of doing business improved from 155 in 2017 to 63 in 2020, and the starting a business’ rank improved from 151 in 2017 to 136 in 2020.
- There is also a behaviour change for the wider lending environment.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code rescued the corporate debtors in a rack that rescued 348 corporate debtors through the resolution plans.
Challenges
- Liquidation– Among the 3,400 cases admitted under the IBC in the last 6 years, more than 50% of the cases ended in liquidation, and only 14% could find a proper resolution.
- Time taken– The average number of days taken to resolve cases increased rapidly over the past five years.
- In FY22, it took 772 days to resolve cases involving companies that owed more than Rs. 1,000 crores.
- Realisation of value– The gap between the realizable values during resolution and liquidation has been narrowing over the years.
- Haircut– A haircut is the debt foregone by the lender as a share of the outstanding claim.
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance in 2021 pointed out that, creditors on an average had to bear an 80% haircut in more than 70% of the cases.
- Conduct of the CoCs– The Standing Committee stated that the committee of creditors has significant discretion in accepting resolution plans and appointing IPs.
Issue with IPs– The IBBI took disciplinary action on 61% of the 203 professionals inspected since 2016, adding that there should be a single regulator for them to ensure best practices and transparency.
SCHEDULE VI Of Indian Constitution
In NEWS:
Recently elections were held for the district autonomous council at Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council (LAHDC)-Kargil. Further, Ladakh post its bifurcation into Union territory has been demanding to be included in the Schedule VI of the Indian constitution.
SCHEDULE VI
Sixth schedule is included under Article 244 (2) and Article 275(1) of the constitution. It delves into the areas declared as ‘tribal areas’ in the states of Assam, Mizoram, Meghalaya and Tripura. It also provides for formation of autonomous district councils for the governance of these areas.
It aims to protect and preserve the tribal culture by providing significant autonomy in administration in the hands of tribal people themselves.
District Autonomous Councils
Tribal areas in these four states have been constituted as autonomous districts but they are included within the executive authority of state.
Composition
- Comprising of maximum 30 members
- Four members nominated governor – hold office during the pleasure of governor
- Rest of the members elected by adult franchise – hold office for a term of five years
A single autonomous district may be inhabited by different tribal groups. In such cases, the autonomous area may be divided further into autonomous regions demarcating areas for each inhabitant tribe. Each autonomous region also has a separate regional council.
| ASSAM | Karbi Anglong district
Bodoland district Dima Hasao district |
| MEGHALAYA | Jaintia hills district
Garo hills district Khasi hill district |
| TRIPURA | Tripura Tribal Areas District |
| MIZORAM | Lai district
Chakma district Mara district |
Legislative power
- They have authority to enact law on
-
- Allotment, occupation or use of land
- Management of forest
- Use of canal or water-course
- Regulation of shifting cultivation
- Establishment of village or town committees or councils
- Other matters relating to village or town administration
- appointment of Chiefs
- Inheritance of property
- Social customs
- All legislation so created must receive approval of governor before taking effect.
Executive power
- They hold authority to establish, construct or manage primary schools, dispensaries, markets, cattle ponds, fisheries, roads, road transport and waterways in the districts as well as prescribe the language and manner of instruction in primary schools.
Judicial power
-
- They are empowered to constitute Village and District Council Courts for the trial of suits and cases with respect to disputes among STs within district.
- But these courts are not given power to decide on cases involving offences punishable by death or imprisonment for five or more years.
Financial power
- They are empowered to
- Prepare budget for their respective council
- Assess and collect land revenue and impose taxes on certain areas
- Grant licence or lease for extraction of minerals within their jurisdiction
Discretionary powers of State Governor
- Organize and reorganize (includes alteration of boundaries) of the tribal regions
- Replace or change the titles of autonomous regions
- Allow or disallow law or development programme to protect self-governance and development needs
- Make regulations for harmony and effective governance of the region
- He Specifies jurisdiction of higher courts on suits and cases held by village council and courts
Acts of parliament or the state legislature do not apply to autonomous regions or apply with specified modifications and exceptions.
Issues
- Extensive rights granted for tribal population hinders the rights of non-tribals in the northeastern states. As a result, many non-tribal people have left these states.
- Grant of partial autonomy has led to frequent conflict of interest and opinion between District council and state legislature.
- Schedule VI along with Inner Line Permit impedes economic growth and contravenes Act East Policy.
Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council
Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council consists of two autonomous district council under the Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council Act of 1995.
-
- Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council (LAHDC)-Leh
- Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council (LAHDC)-Kargil
These autonomous regions are created by separate legislation outside the purview of Schedule VI.
Ladakh has been enthusiastic to be included in Schedule VI due to
-
- Buddhist dominated Leh district felt neglected in the erstwhile state government
- Fears in the region about land, demography and cultural identity
- Limited financial powers accorded to the councils under the present act
Other News
| Urban unemployment rate drops |
|
| ICMR to conduct study to develop solutions to remedy childhood undernutrition |
|
| Nobel Prize |
|
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs


