
Intellectual property deals with the human capital applied for creativity and inventions. Intellectual Property Rights are legal rights given to a creator or innovator to enjoy the economic benefits of their invention or creation. These are territorial rights registered with a legal authority. It provides a secure environment for investors, scientists, artists, designers, traders etc. and fosters innovation and scientific temper in the country.
Types of Intellectual Property Rights
On the basis of type of invention or creation and their application, the IPRs are classified as
- Patents
- An exclusive right granted for a product or a process
- It generally entails a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem.
- Criteria for patentability are usefulness, novelty and non-obviousness.
- It provides protection for a period of 20 years.
- Patent regime in India cover protection of plant varieties & farmer’s rights and protection of traditional knowledge through Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001 and The Biological Diversity Act.
- Trademarks
- A distinctive sign which differentiates goods or services produced or provided by a specific person or enterprise from others
- It may be one or a combination of words, letters, and numerals.
- Copyright and related rights
- A legal term describing rights given to creators for their literary and artistic works.
- Creators often sell these rights to individuals or companies in return for payment dependent on the actual use of the work. This is referred to as royalties.
- Geographic indications of source
- A sign used on goods that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities, reputation or characteristics that are essentially attributable to that place of origin.
- It is governed by The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- Industrial designs
- A novel or original design that is accorded to the proprietor of a validly registered design.
- It protects the unique appearance of a product.
- It is regulated by the New Designs Act, 2000 which provides more detailed classification of design in line with international system.
- Trade Secrets
- In general, any confidential business information that provides an enterprise a competitive edge may be considered a trade secret.
- The unauthorized use of such information by persons other than the holder is regarded as an unfair practice and a violation.
- Unlike patents, these are protected without registration.
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuit of Layout Designs (SICLD)
- The SICLD Act of 2000 provides the registered proprietor of a layout-design an inherent right to use, commercially exploit and obtain relief in case of infringement.
- The SICLD Act of 2000 provides the registered proprietor of a layout-design an inherent right to use, commercially exploit and obtain relief in case of infringement.
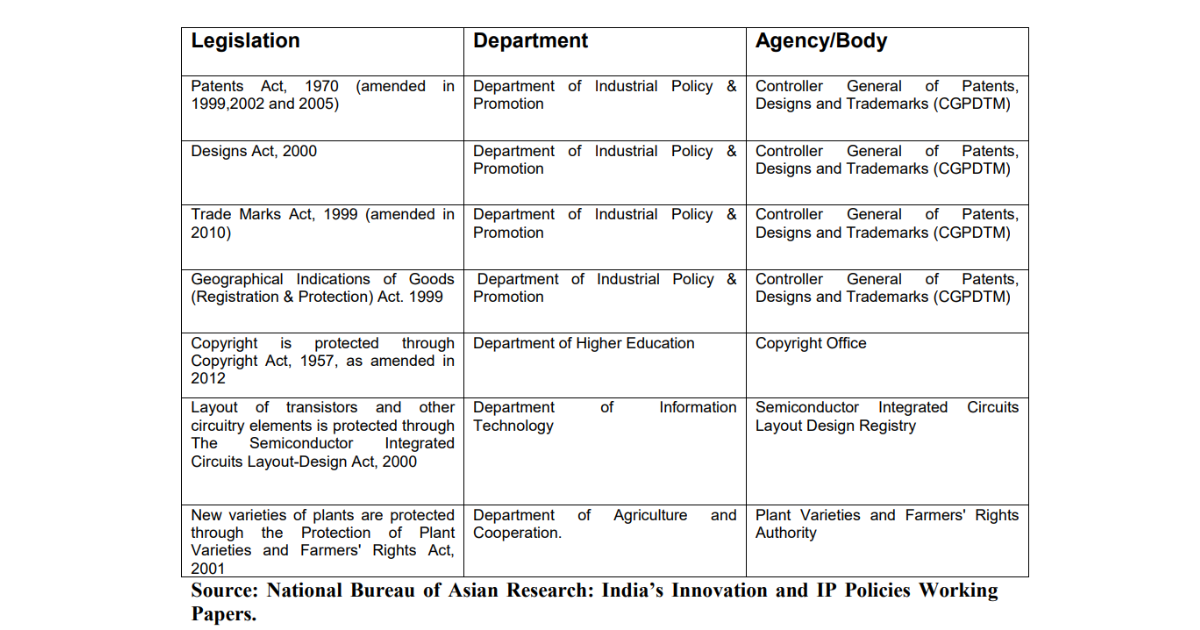
National Intellectual Property Rights Policy
This policy aims to integrate Intellectual Property as a policy and strategic tool in national development plans. It foresees the need for a holistic approach and the development of a coordinated and integrated development of Intellectual Property system focussed on legal, administrative, institutional and enforcement related matters.
The Policy lays down seven objectives
- IPR Awareness : Outreach and Promoton – To create public awareness about the economic, social and cultural benefts of IPRs among all sectons of society
- Generaton of IPRs : To stmulate the generaton of IPRs
- Legal and Legislatve Framework: To have strong and efectve IPR laws, which balance the interests of rights owners with larger public interest
- Administraton and Management : To modernize and strengthen serviceoriented IPR administraton
- Commercializaton of IPR : Get value for IPRs through commercialization
- Enforcement and Adjudicaton : To strengthen the enforcement and adjudicatory mechanisms for combatng IPR infringements
- Human Capital Development : To strengthen and expand human resources, insttutons and capacites for teaching, training, research and skill building in IPRs
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs