GS 3-Infrastructure
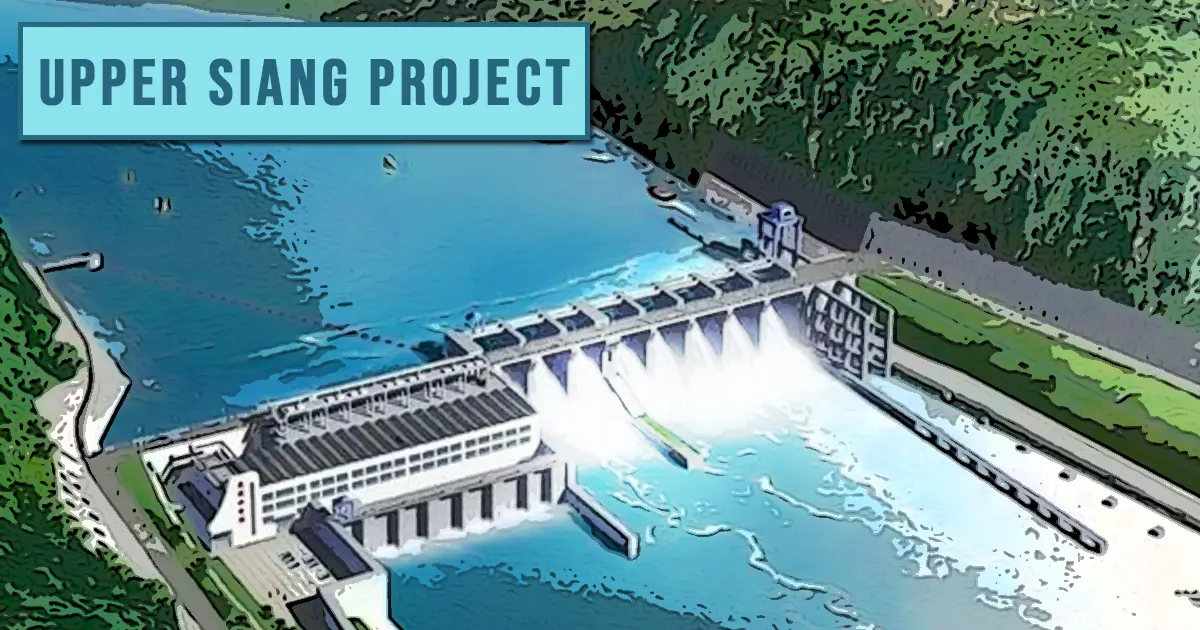
The Upper Siang Multipurpose Storage Project is a proposed 11,000 MW hydropower project on the Siang River in Arunachal Pradesh, developed by the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC).
- It will be India’s largest hydropower project upon completion.
- The project is aimed at countering China’s plans to divert the flow of the Yarlung Tsangpo River, which flows as Siang in Arunachal Pradesh and Brahmaputra in Assam.
Objectives
- Strategic Water Security: Mitigate risks associated with China diverting the river’s natural flow.
- Flood Management: Reduce flooding in the Brahmaputra River.
- Water Storage: Store 9 billion cubic meters of water to support irrigation needs in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
Hydropower Potential in Arunachal Pradesh
- Geographic Advantage: Hilly terrain and high annual rainfall create ideal conditions for hydropower.
- River Basins: The state has eight major river basins, including Siang, Subansiri, and Lohit, offering abundant opportunities for hydropower.
- Potential: Arunachal Pradesh accounts for about 40% of India’s total hydropower potential, estimated at over 58,000 MW, though less than 1% has been utilized.
Key Hydroelectric Projects
- Kameng Hydroelectric Project: On Kameng River.
- Subansiri Upper Hydroelectric Project: On Subansiri River.
- Siang Lower Hydroelectric Project: On Siang River.
- Hirong Hydroelectric Project: On Siyom River.
Challenges and Opposition
Habitat Destruction and Displacement
- Threatens habitats of local communities, especially the Adi tribe.
- Several villages, including the Upper Siang district headquarters Yingkiong, may face submergence.
Environmental Impacts
- Large-scale deforestation for land acquisition.
- Adverse effects on ecosystems, wildlife habitats, and biodiversity.
- Example: Hydropower projects in Uttarakhand have worsened climate-related issues, leading to cloudbursts and flash floods.
Economic Effects
- Loss of rivers as a source of livelihood and cultural significance for local communities.
Social Impacts
- Tribal displacement could disrupt cultural and social dynamics in the region.
Protests and Precedents
- Local Protests: Focused on environmental degradation, displacement, and loss of livelihood.
- Similar Cases:
- In Himachal Pradesh, campaigns like ‘Save Kinnaur’ and ‘No Means No’ oppose hydropower expansion.
- In Uttarakhand, uncontrolled construction has caused landslides, endangering lives and ecosystems.




