
Introduction
Microfinance is a method of lending very small sums to individuals to start or expand a small business. These borrowers tend to be low-income individuals.
Features of Microfinance in India
- The principal amount borrowed is less than Rs 1 lakh
- Interest rates are lower than normal banks
- Does not require collateral for loan
- Issued to households with an annual income of up to Rs 3 lakh.
Micro Finance Institution- MFI
Microfinance Institutions are financial institutions that offer small loans to borrowers without access to banking services. Their services include microloans, micro savings, microinsurance, etc.
Objectives of Microfinance Institutions
- Offers support to the lower strata of society.
- Encourage rural entrepreneurship and self-employment generation
- Adopting an effective strategy to help eradicate poverty
- Ensure financial inclusion and accelerate the development process
- Improvise the skill set among rural people
Types of Microfinance Institutions
- Joint Liability Group (JLL)
- Self-Help Group (SHG)
- Regional Rural Bank
- Cooperatives
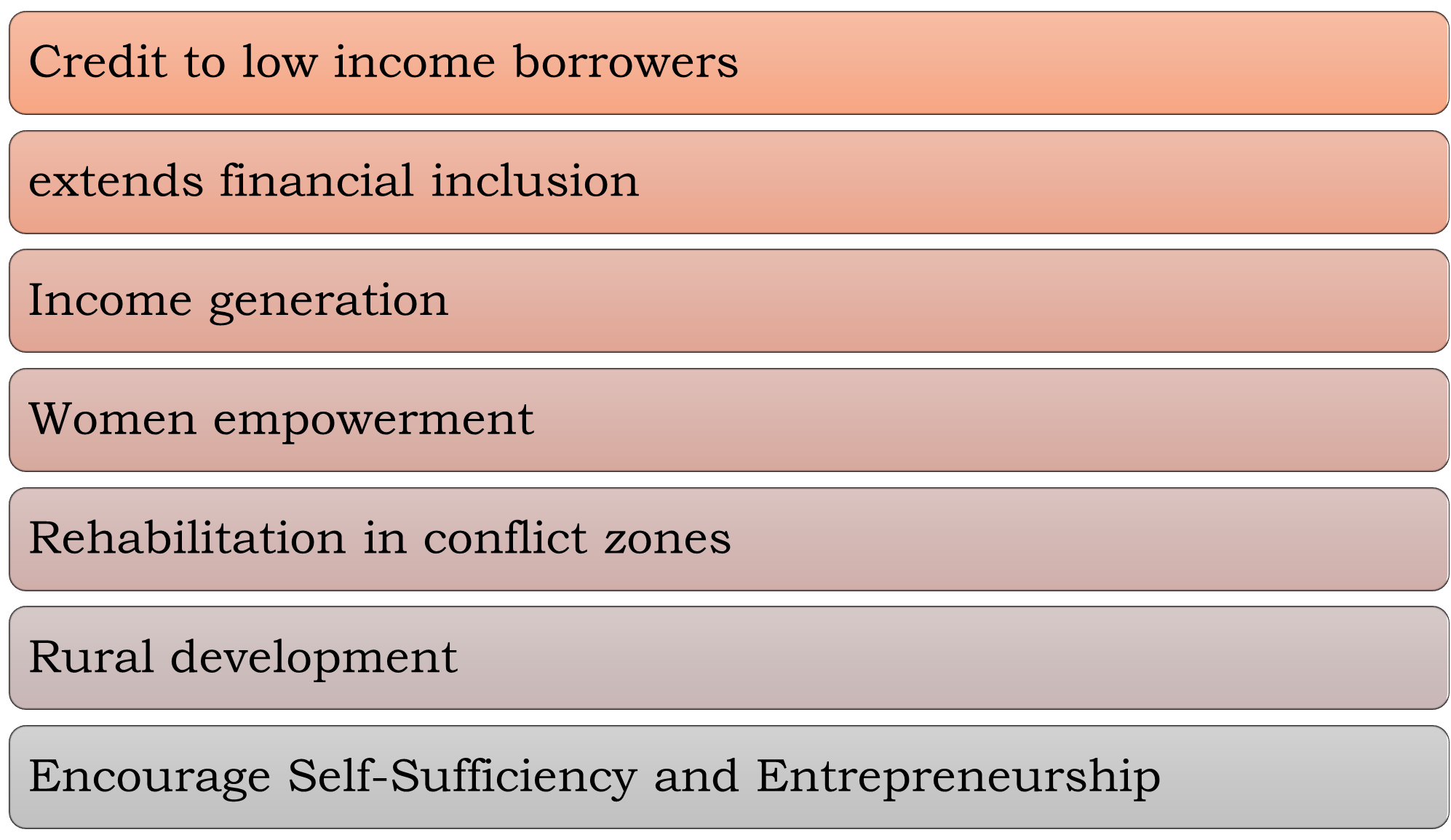
Benefits of Microfinance
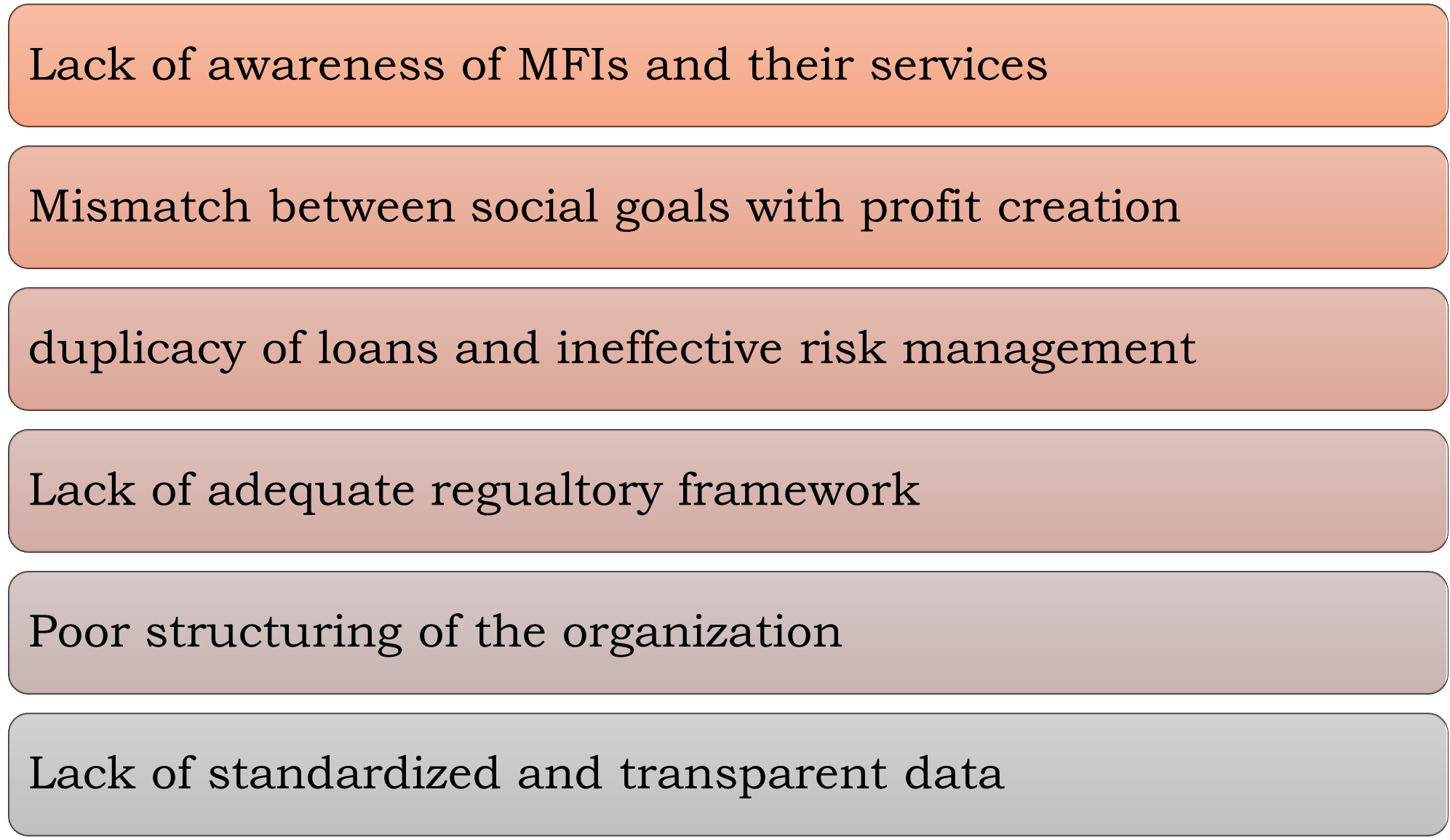
Challenges Faced
Initiatives undertaken
Government Programmes
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme (SHG-BLP)
- Initiated by NABARD in 1992, this model especially incentivises women’s self-help group to unite mobilize resources to avail loans and other banking services.
- Micro Enterprise Development Programme (MEDPs) & Livelihood and Enterprise Development Programme (LEDP)
- The programme enables SHG members to be up-skilled to take up income generating livelihood activities.
- Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
- It implements the credit guarantee scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises which is extended to microfinance institutions as well.
- Financial Support by NABARD and SIDBI
- NABARD provides Revolving Fund Assistance (RFA) while SIDBI aids through SIDBI Foundation for Micro Credit (SFMC), India Microfinance Equity Fund (IMEF)
- Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd (MUDRA)
- Support to Microfinance sector was scaled up by Government of India by setting up MUDRA in 2015.
Regulatory Initiatives
- Y H Malegam Committee
- In the wake of AP Microfinance crisis in 2010, it was constituted by the RBI to study issues and concerns in the Microfinance sector
- Introduction of Regulations for NBFC-MFIs
- A comprehensive regulatory framework including eligibility criteria for loans for NBFC-MFIs was introduced in 2011 based on the Malegam Committee recommendations.
- Regulatory Framework for Microfinance Loans
- RBI has implemented Regulatory Framework for Microfinance Loans, effective from April 1, 2022, to update Microfinance regulatory policy.
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
