 India is among a select group of seven nations that possess intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and is one of just four countries that boast anti-ballistic missile systems.
India is among a select group of seven nations that possess intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and is one of just four countries that boast anti-ballistic missile systems.
This places India in an exclusive category of nations that have developed advanced missile capabilities capable of long-range targeting and defence against incoming ballistic missiles. The acquisition of such advanced military technology is a testament to India’s prowess in the field and highlights its commitment to maintaining a robust national defence posture.
India’s missile development program has grown significantly in recent years. India is now one of the top missile manufacturers in Asia, if not the world.
India has developed, tested, and operationalized several missile systems, including:
- Hypersonic technology missiles
- Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM)
- Anti-satellite weapon (ASAT)
- Submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM)
FOUR MAJOR MISSILE CONTROL REGIMES
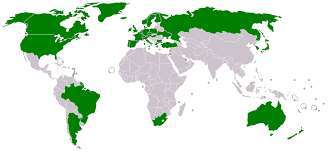
Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG)
NSG was formed with the objective of averting the proliferation of nuclear weapons and preventing acts of nuclear terrorism. NSG consists of 48 members which include the five nuclear weapon states US, UK, France, China, and Russia. It is not a formal organization, and its guidelines are not binding. Decisions, including on membership, are made by consensus
The NSG’s objectives include
- Curb the export of nuclear weapons development materials and related technology
- Improve the existing safeguards on existing nuclear materials
- Ensure that nuclear exports are carried out with appropriate safeguards, physical protection, and nonproliferation conditions
- Restrict the export of sensitive items that can contribute to the proliferation of nuclear weapons
- Ensure that nuclear trade for peaceful purposes does not contribute to the proliferation of nuclear weapons or other nuclear explosive devices
- Ensure that international trade and cooperation in the nuclear field is not hindered unjustly in the process
India is not member of Nuclear Suppliers Group as India is not signatory to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. But India’s record on commitment to non proliferation and transparency maintained with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) stand as factors favourable to India’s inclusion into the group. Membership to the NSG will essentially increase India’s access to state-of-the-art technology from the other members of the Group.
Missile Technology Control Regime
The Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) is an informal, non-treaty organization of governments with common interests in missile, unmanned air vehicle, and related technology nonproliferation. It was established in 1987 and unites 35 countries engaged in the supply of missile technology.
Objectives include
- Their objective is to limit risks of proliferation by controlling transfers to delivery systems capable of weapons of mass destruction.
- It maintains watch over the transfer of missile equipment, material, and related technologies capable of delivering weapons of mass destruction to fight this threat.
- It is particularly concerned with rockets and unmanned aerial vehicles capable of delivering a payload of at least 500 kg across a range of at least 300 km, as well as the associated equipment, software, and technology.
- The objectives of MTCR are achieved through export restriction, meetings, and outreach & dialogue.
Wassenaar Agreement
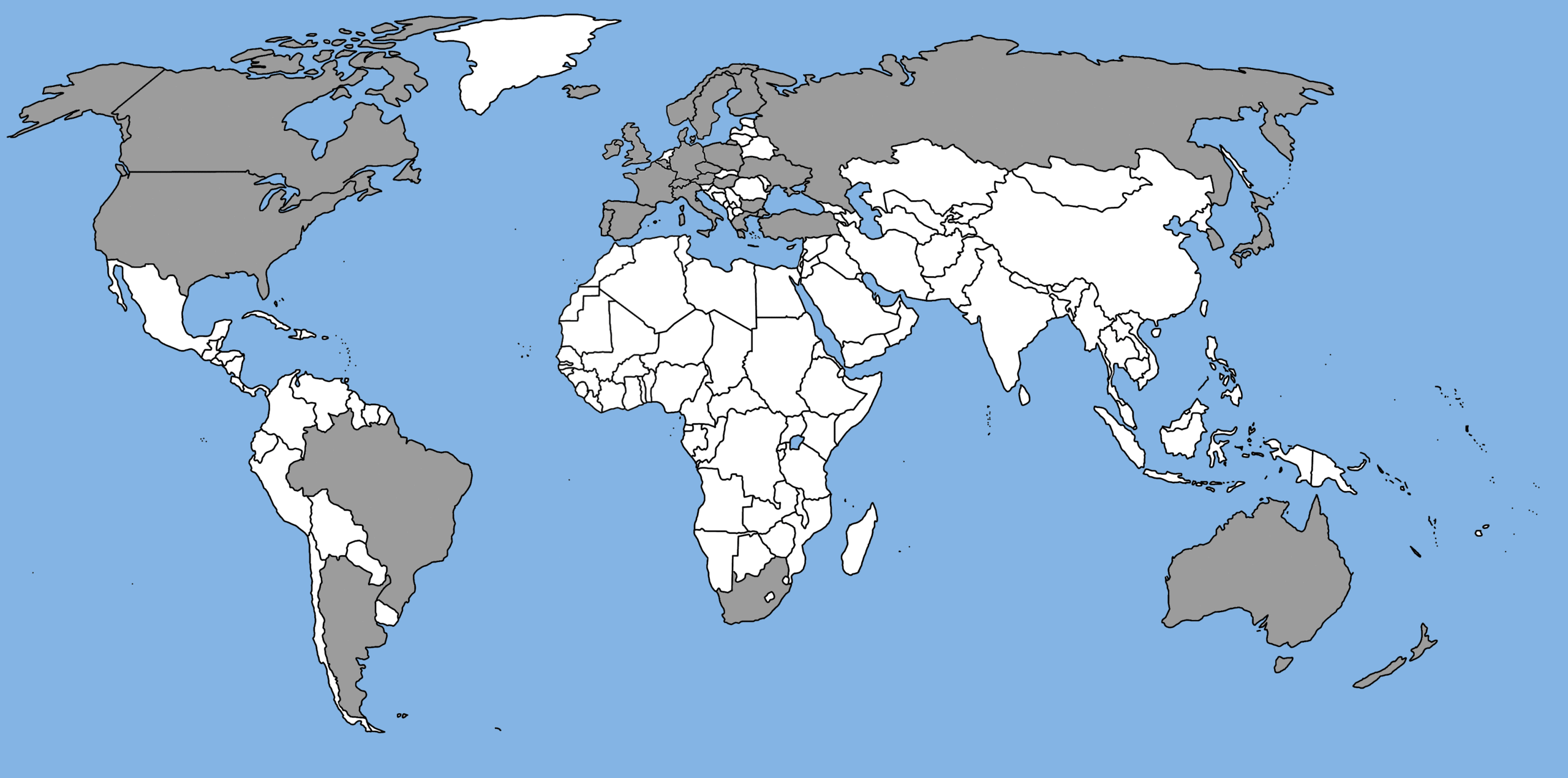
Objectives of the arrangement
- Contributes to regional and international security and stability
- Promotes transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies
- Complements and reinforces the export control regimes for weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems
- Is not directed against any state or group of states
- Uses export controls as a means to combat terrorism
Participating States through their national policies ensure that transfers of these items do not contribute to the development or enhancement of military capabilities which undermine these goals and also prevents the acquisition of these items by terrorists.
Participating states must
- maintain national export controls on items included in the WA Control Lists
- be guided by agreed Best Practices, Guidelines or Elements
- report on transfers and denials of specified controlled items to destinations outside the Arrangement
- exchange information on sensitive dual-use goods and technologies
India is signatory to the agreement.
Australia Group
It is a voluntary, informal export-control agreement through which 42 nations, along with the European Union, founded in 1985.
The objectives of Australia Group are as follows:
- The main goal is to prevent the spread of chemical or biological weapons by using licensing mechanisms to prevent the export of specific production facilities and equipment.
- It coordinates the national export licensing regulations of the participating nations.
- The group members also seek to ensure that industries in their countries do not attempt to spread biological and chemical weapons.
India joined the Australian group in 2018. Admission to the group would strengthen supply chain security in the burgeoning biotechnology industry and establish credentials to join the NSG, the only export control group to which it is not a member.
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs