
The story so far:
Bangladesh’s Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina returned to power for a historic fourth consecutive term earlier this month they won two-thirds of the seats in the January 7 national elections. Prime Minister Narendra Modi was among the first world leaders to congratulate Ms. Hasina, highlighting the close bilateral relationship between the two countries.
How have relationships flourished?
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War served as the foundation for India’s relationship with Bangladesh.
- India provided critical military and material support to Bangladesh during its fight for independence from Pakistan.
Despite this, relations deteriorated after a few years as military regimes took power. In the mid-1970s, anti-India sentiment increased due to issues ranging from boundary disputes and insurgency to water-sharing.
- The instability lasted several decades until Sheikh Hasina took power in 1996 and signed a treaty to share Ganga waters, ushering in a new chapter in bilateral relations.
Since then, India and Bangladesh have developed partnerships in trade, energy, infrastructure, connectivity, and defence.
Economic cooperation
Bilateral trade between India and Bangladesh has steadily increased over the last decade. Bangladesh has emerged as India’s largest trade partner in South Asia, with bilateral trade rising to $18 billion in 2021-2022 from $10.8 billion in 2020-21, though there was a drop in 2022-23 due to the pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war. India is also Bangladesh’s second largest trade partner, with $2 billion in exports to Indian markets.
In 2022, both nations concluded an integrated feasibility study on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA). The agreement, which is typically intended to reduce or eliminate customs duties on traded goods and simplify trade rules, is expected to create new social and economic opportunities. The CEPA is especially important because Bangladesh is set to lose its Least Developed Country (LDC) status after 2026, resulting in the loss of duty-free and quota-free market access in India. Dhaka will be eager to finalise a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with New Delhi while also pursuing the China-backed Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). This dual approach raises concerns in India.
Infrastructural Development
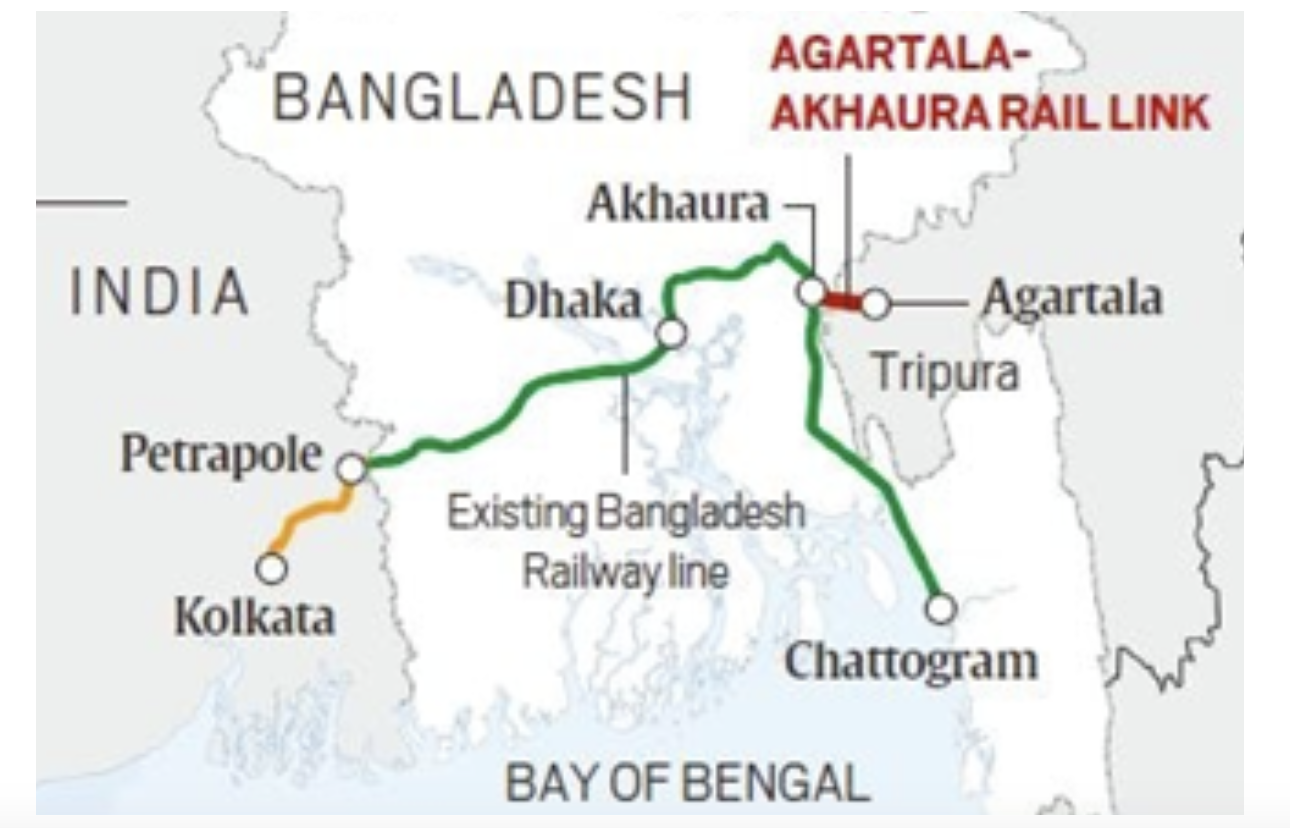
As a “major development partner” of Bangladesh, India is funding several infrastructure and connectivity projects. Since 2010, India has extended Lines of Credits worth over $7 billion. PM Modi and Sheikh Hasina made history last year when they inaugurated the Akhaura-Agartala rail link that connects Bangladesh and the northeast through Tripura. The link has given India access to Chattogram and Mongla ports in Bangladesh for the movement of cargo. It is likely to boost small-scale industries and develop Assam and Tripura.
In the energy sector, Bangladesh imports almost 2,000 megawatts of electricity from India. The BIMSTEC Master Plan for Transport Connectivity aims to connect major transport projects in India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand, forming a shipping network. India’s attention will be focused primarily on Bangladesh’s Matarbari Port, which is being built about 100 kilometres from Tripura. The port will create a critical industrial corridor connecting Dhaka to northeast India.
Area of tension
- The looming Teesta dispute will take centre stage on the agenda of Hasina’s government. The issue is the sharing of Teesta’s waters, with Bangladesh seeking a fair distribution.
- Another contentious issue is the Rohingya situation. The Hasina government seeks the peaceful repatriation of Rohingyas to Myanmar, but talks with the military junta have thus far been unsuccessful. Bangladesh seeks India’s help in influencing Myanmar, but the Modi government, which has ties to the junta, claims it will deport Rohingyas from its mainland.
- Cross-border terrorism and infiltration pose additional threats to internal security. The rise of majoritarian forces adds another layer to the already complex landscape.
Global ties
In 2021, the Biden administration-imposed sanctions on a Bangladeshi anti-crime and anti-terrorism task force, citing human rights violations, and heightened tensions by announcing a policy to restrict visas for Bangladeshis it believes are undermining the country’s election process. Adding to India’s concerns is the growing relationship between Bangladesh and China, as evidenced by significant Chinese infrastructure investments in recent years.
- According to the Chinese Ambassador to Bangladesh, China built 12 highways, 21 bridges, and 27 power and energy projects in the country.
- However, Ms. Hasina has maintained that her government is “very much careful” about its partnership with China.
Prelims Bytes:
1.The Mpemba effect– named after Tanzanian student Erasto Mpemba, who brought attention to this counterintuitive phenomenon in 1969, makes for curious observation. The effect is that hot water can freeze faster than cold water in similar conditions.
2.Gambusia affinis and Gambusia holbrooki– Mosquitofish, used to fight mosquitoes, has become invasive in India.It is the native species of the southeastern united states.
3.NISAR-The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission, an ISRO-NASA collaborative effort, is expected to launch in the first quarter of 2024 as planned.
- NISAR is a Low Earth Orbit observatory that shows international cooperation in space exploration. It was created by NASA and ISRO together.
- The mission is scheduled to launch by ISRO’s GSLV Mark-II launch vehicle from Srihari Kota’s Satish Dhawan Space Centre.
- Researchers will benefit from the extraordinary detail provided by NISAR data in a number of ways, such as tracking the consequences of groundwater use, analysing the rate of ice sheet melt, monitoring volcanic activity, and detecting changes in the geographical distribution of vegetation around the world.
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
