
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living species on Earth, including plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi.
While Earth’s biodiversity is so rich that many species have yet to be discovered, many species are being threatened with extinction due to human activities, putting the Earth’s magnificent biodiversity at risk. Biosphere reserves are designated by UNESCO and are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
Three Zones of a Biosphere Reserve:
Biosphere reserves are customarily divided into three interconnected zones, referred to as the core region, the buffer zone, and a transition area or “area of cooperation,” in order to carry out the complementary tasks of biodiversity protection and sustainable resource use.
Core Areas
- Incorporates protected areas, which serve as benchmarks for the original conditions of the ecosystems that the biosphere reserves reflect.
- Data derived from these fundamental domains can be employed to evaluate the sustainability of operations or the preservation of environmental standards in adjacent regions.
- Projects created in collaboration with biosphere reserve residents, companies, and other partners may receive funding from the core area managers.
Buffer zones
- Encircles or borders the central region.
- The way these activities are planned makes sure that they support, rather than undermine, the core area’s conservation goals.
- The buffer zone may be used for experimental research, or it may involve managing ranchlands, farms, forests, fisheries, and natural vegetation to improve total productivity while preserving biodiversity and natural processes.
- Facilities for tourism, education, training, and recreation may also be located in this zone.
- The buffer zone is viewed in many biospheres reserves as having less extensive human use than the transition area may have.
Transition area or “area of cooperation”
- The sizable exterior region of a biosphere reserve where people reside and work while sustainably utilising the local natural resources.
- The phrase “area of cooperation” emphasises how important collaboration is in achieving the goals of the biosphere reserve.
- Here, the local communities, businesses, scientists, civil associations, cultural organisations, conservation agencies, and other interested parties come to an agreement to collaborate in order to manage and use the environment in a way that will benefit the local population in a sustainable manner.
How biosphere reserves are used to promote sustainable development?
Sustainable agriculture
- Biosphere reserves can support sustainable agriculture practices that help to protect biodiversity and improve the livelihoods of local communities.
- For example, the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve in India supports farmers in developing organic farming practices.
Tourism
- Biosphere reserves can be used to promote sustainable tourism that generates income for local communities and helps to conserve biodiversity.
- For example, the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve in India supports community-based tourism projects that provide employment and income opportunities for local fishermen and women.
Education and awareness
- Biosphere reserves can be used to educate and raise awareness of the importance of biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
- For example, the Sunderbans Biosphere Reserve in India offers educational programs for school children on the importance of mangrove forests.
Biosphere reserves – research and development
Providing sites for long-term research
- Biosphere reserves are protected areas that are typically large and diverse, making them ideal for long-term research on ecological and social systems.
- This research can help scientists to better understand how these systems work and how to manage them sustainably.
Facilitating interdisciplinary research
- Biosphere reserves are often home to a variety of stakeholders, including scientists, land managers, and community members.
- This diversity of perspectives can facilitate interdisciplinary research that addresses complex challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
Supporting the development of sustainable practices:
- Biosphere reserves are intended to be model sites for sustainable development.
- Research conducted in biosphere reserves can help to develop and demonstrate new sustainable practices that can be adopted by other communities around the world.
Examples of how biosphere reserves are being used to promote research and development
The Great Smoky Mountains Biosphere Reserve in the United States, scientists are studying the effects of climate change on forest ecosystems.
- TheSian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve in Mexico, researchers are working with local communities to develop sustainable fishing practices.
- The Nilgiri Biosphere Reservein India, scientists are studying the interactions between human and elephant populations.
- The Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve in Romania, researchers are developing new methods for managing wetlands in the face of sea level rise.
There are 18 biosphere reserves in India, each of which is a unique and valuable ecosystem. These reserves protect a wide range of biodiversity, from the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the coral reefs of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
| Biosphere Reserve | States | Ecosystem |
| Achanakmar-Amarkantak | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh | Tropical moist deciduous forest |
| Agasthyamala | Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka | Tropical moist evergreen forest |
| Cold Desert | Himachal Pradesh | Trans-Himalayan cold desert |
| Dehang-Debang | Arunachal Pradesh | Alpine meadows, temperate forests |
| Dibru-Saikhowa | Assam | Riverine grasslands, swamp forests, tropical moist deciduous forest |
| Gulf of Mannar | Tamil Nadu | Marine ecosystem |
| Khangchendzonga | Sikkim | Temperate forests, alpine meadows, glaciers |
| Manas | Assam | Tropical moist deciduous forest, grasslands |
| Nanda Devi | Uttarakhand | Alpine meadows, temperate forests, glaciers |
| Nilgiri | Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka | Tropical moist evergreen forest, grasslands |
| Nokrek | Meghalaya | Temperate forests, bamboo forests |
| Pachmarhi | Madhya Pradesh | Tropical moist deciduous forest, grasslands |
| Panna | Madhya Pradesh | Tropical dry deciduous forest |
| Simlipal | Odisha | Tropical moist deciduous forest, grasslands |
| Seshachalam | Andhra Pradesh | Tropical moist deciduous forest |
| Sunderbans | West Bengal | Mangrove forest, mudflats, tidal rivers |
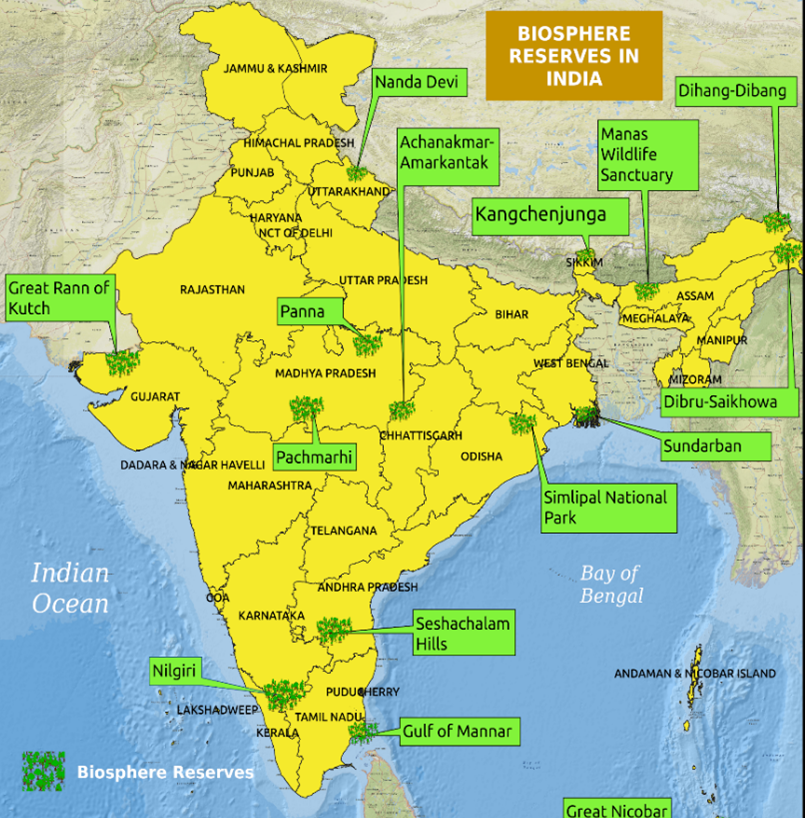
Biosphere reserves play an important role in protecting India’s biodiversity and natural heritage. They also provide economic benefits to local communities through sustainable tourism and the harvesting of non-timber forest products.
In addition to the 18 biosphere reserves, there are a number of other potential sites that have been identified by the Ministry of Forests and Environment. These sites include:
- The Abujmarh Biosphere Reserve in Chhattisgarh
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands North Islands Biosphere Reserve
- The Chintapalli Biosphere Reserve in Andhra Pradesh.
The Indian government is committed to the conservation of biosphere reserves and has taken a number of steps to protect these important ecosystems. These steps include:
- The establishment of management committees
- The development of conservation plans
- The provision of funding for research and education.
Functions : Conservation, Sustainable Development, Logistics Support
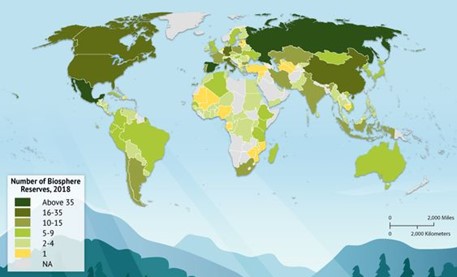
The distribution of biosphere reserves across the world
- Africa: 85 sites in 31 countries
- Arab States: 33 sites in 12 countries
- Asia and the Pacific: 157 sites in 24 countries
- Europe and North America: 309 sites in 41 countries
- Latin America and the Caribbean: 134 sites in 22 countries
Top 5 countries with the most biosphere reserves
| Rank | Country | Number of biosphere reserves |
| 1 | Spain | 73 |
| 2 | China | 59 |
| 3 | Mexico | 48 |
| 4 | Russia | 50 |
| 5 | Peru | 48 |
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves is a UNESCO program that promotes cooperation and collaboration between biosphere reserves around the world. The network is also a valuable resource for sharing knowledge and best practices for conservation and sustainable development.
Read Further
Other NEWS:
| 2+2 dialogue | A 2+2 dialogue is a diplomatic summit where two appointed ministers from each country meet to discuss their strategic and security interests.
The goal is to enhance high-level engagements on bilateral, regional, and global issues. India has 2+2 dialogues with four key strategic partners:
|
| Electoral literacy content in NCERT textbooks |
|
| Putin signs Bill revoking Russia’s ratification of global nuclear treaty |
|
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
