
Ayodhya, a city in Uttar Pradesh, India, is steeped in art and culture, deeply intertwined with the Hindu epic Ramayana and the worship of Lord Rama. A grand temple dedicated to Lord Rama.
Ram Mandir:
Architecture:
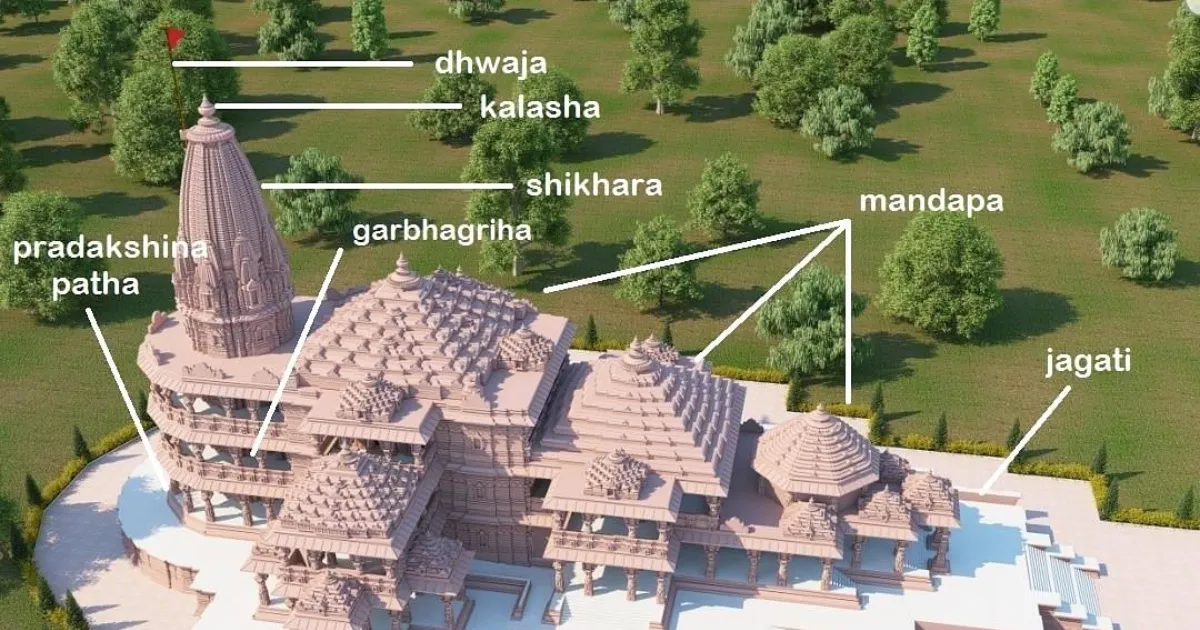
The temple is being built in the Nagara style, characterized by its towering shikhara (spire) and intricate carvings. The three-story structure will feature 366 columns, an octagonal sanctum sanctorum, and a prayer hall that can accommodate thousands of devotees.
Sculpture and Murals:
The temple walls will be adorned with intricate sculptures and murals depicting scenes from the Ramayana, showcasing skilled artisanship and storytelling through art.
Significance:
The Ram Mandir is not just a religious monument but also a cultural symbol representing the faith and traditions of millions of Indians. Its construction has been a unifying factor and a source of national pride.
Beyond the Ram Mandir:
Hanuman Garhi:
This ancient temple dedicated to Lord Hanuman, Rama’s loyal monkey companion, is another major pilgrimage site in Ayodhya. The temple’s flag is said to change direction according to the wind, signifying Hanuman’s ever-watchful presence.
Kanak Bhavan:
This palace, believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama, is an archaeological site with remnants of ancient structures and sculptures.
Sita Ki Rasoi:
This temple marks the spot where Sita, Rama’s wife, is said to have prepared meals for their followers.
Ram Katha:
The tradition of storytelling through recitation of the Ramayana is deeply ingrained in Ayodhya’s culture. Visitors can experience this tradition through evening gatherings or attend special Ram Katha performances.
Folk Art:
Ayodhya is known for its vibrant folk-art forms, including embroidery, pottery, and puppetry, often depicting scenes from the Ramayana or showcasing local legends.
Additionally:
- The city hosts several festivals throughout the year, including Ram Navami, Diwali, and Dussehra, which celebrate the life and deeds of Lord Rama and showcase the city’s vibrant cultural traditions.
- Ayodhya is also home to several museums and art galleries that showcase the region’s artistic heritage and historical significance.
Nagara Style Architecture
The Crown Jewel of North Indian Temple Architecture
It is a symphony of soaring heights, intricate carvings, and profound symbolism. This style, distinct from the Dravidian style of South India, has graced the landscape for centuries, adorning temples with a unique elegance and spiritual energy.
Hallmarks of the Nagara Style:
The Shikhara:
The shikhara, is a curvilinear tower rising majestically above the sanctum sanctorum (garbhagriha). Imagine a graceful, upward-spiraling form, often segmented with horizontal bands and adorned with intricate sculptures, culminating in a crowning amalaka (disc) and kalasha (pot). Think of the iconic Khajuraho temples or the Sun Temple at Modhera – their breathtaking shikharas exemplify the Nagara style’s grandeur.
The Mandapa:
The mandapa, or pillared hall, serves as a gathering space for devotees. In Nagara temples, it typically sits on a raised platform and features intricately carved pillars and ceilings. Imagine the intricately carved mandapa of the Somnath Temple, where sunlight filters through ornate latticework, creating a mesmerizing play of light and shadow.
The Amalaka and Kalasha:
These crowning elements atop the shikhara holds deep symbolism. The amalaka, a ribbed disc, represents the base of the universe, while the kalasha, a pot-like structure, symbolizes prosperity and the containment of celestial energy. Together, they mark the culmination of the temple’s spiritual ascent.
Variations within the Style:
The Nagara style, like any vibrant artistic tradition, encompasses diverse regional variations. From the steep, curvilinear shikharas of the Odisha school to the gently rising towers of the Gujarat Solanki style, each region infuses the Nagara with its own unique charm.
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs