India announced its recognition of Israel on September 17, 1950. Soon thereafter, the Jewish Agency established an immigration office in Bombay. This was later converted into a Trade Office and subsequently a Consulate. Embassies were opened in 1992 when full diplomatic relations were established.
Since the upgradation of relations in 1992, defence and agriculture formed the two main pillars of our bilateral engagement. In recent years, relations have seen rapid growth across a broad spectrum of areas and the future vision of the cooperation is of a strong hi-tech partnership as befits two knowledge economies.
Agreements
- Increased high-level exchanges and ministerial visits on both sides have expanded cooperation in different functional areas such as trade, agriculture, S&T,culture and security, after 2015.
- On July 2017, after the visit of Indian PM for the first time to Israel – during which the relationship was upgraded to a strategic level and seven Agreements/MoUs were signed in the fields of R&D innovation, water, agriculture and space.
- On January 2018, after the visit of Israel to India – four G2G agreements on cyber security, oil & gas cooperation, film co-production and air transport were signed, along with five other semi-government agreements.
Economic and Commercial Relations
- Up to January 2023, trade between India and Israel is expected to reach roughly USD 7.5 billion, up from USD 5 billion before the Covid-19 pandemic.
- About 50% of bilateral trade is made up of diamond trade.
- India is Israel’s seventh-largest trading partner worldwide and third-largest in Asia.
- Israeli businesses have made investments in India in the areas of energy, renewable energy, telecom, real estate, and water technology. They are now concentrating on establishing R&D facilities or manufacturing facilities there.
- India and Israel are in discussions to finalize a free trade agreement (FTA).
Agriculture
- India has benefited from Israeli expertise and technologies in horticulture mechanization, protected cultivation, orchard and canopy management, nursery management, micro- irrigation and post-harvest management.
- Israeli drip irrigation technologies and products are now widely used in India.
- A comprehensive Work Plan for cooperation in agriculture was signed in 2006.
- Agricultural cooperation between the two sides formalized through 3-year Work plans wherein 3-year Action plans are developed.
- Centres of Excellence have been constituted in Indian states.
Defence & Security
India imports critical defence technologies from Israel.
-
- The last major visit from the Indian side was that of the Chief of Air Staff visited Israel from 22-24 May 2018 to attend the multilateral conference of Air Chiefs & Commanders.
- Defence & Security – India imports critical defence technologies from Israel. *
- There is cooperation on security issues, including a Joint Working Group on Counter-Terrorism.
- Since 2015, IPS officer trainees have been visiting the Israel National Police Academy every year for 1-week long foreign exposure training.
Cooperation in S&T and Space
- India-Israel cooperation in S&T is overseen by the Joint Committee on S&T, established under the S&T Cooperation Agreement signed in 1993.
- Its last meeting took place in March 2019 in Israel.
- MoU for establishing India-Israel Industrial R&D and Innovation Fund (I4F) by the Department of Science and Technology, India and the National Authority for Technological Innovation, Israel was signed on July 2017
- This MoU, with a contribution of $ 20 m from each side over 5 years.
- Space agencies-ISRO & Israel Space Agency- signed three agreements on space cooperation in July 2017
Indian Community
- There are approximately 85,000 Jews of Indian-origin in Israel (with at least one Indian parent), who are all Israeli passport holders.
- The main waves of immigration into Israel from India took place in the fifties and sixties
- There are about 14,000 Indian citizens in Israel, of whom around 13,200 are care-givers employed by Israeli elders to take care of them. Others include diamond traders, some IT professionals and students.
GLOBAL HUNGER INDEX
Context
India ranks 111 out of 125 countries in Global Hunger Index
Global Hunger Index is an annual report measuring and tracking hunger at global, regional and national levels. It is released by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe.
Four indicators utilized are:
Undernourishment: the share of the population with insufficient caloric intake.
Child stunting: the share of children under age five who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition.
Child wasting: the share of children under age five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition.
Child mortality: the share of children who die before their fifth birthday, partly reflecting the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
India scored 28.7 on GHI showcasing serious levels of hunger as per report.
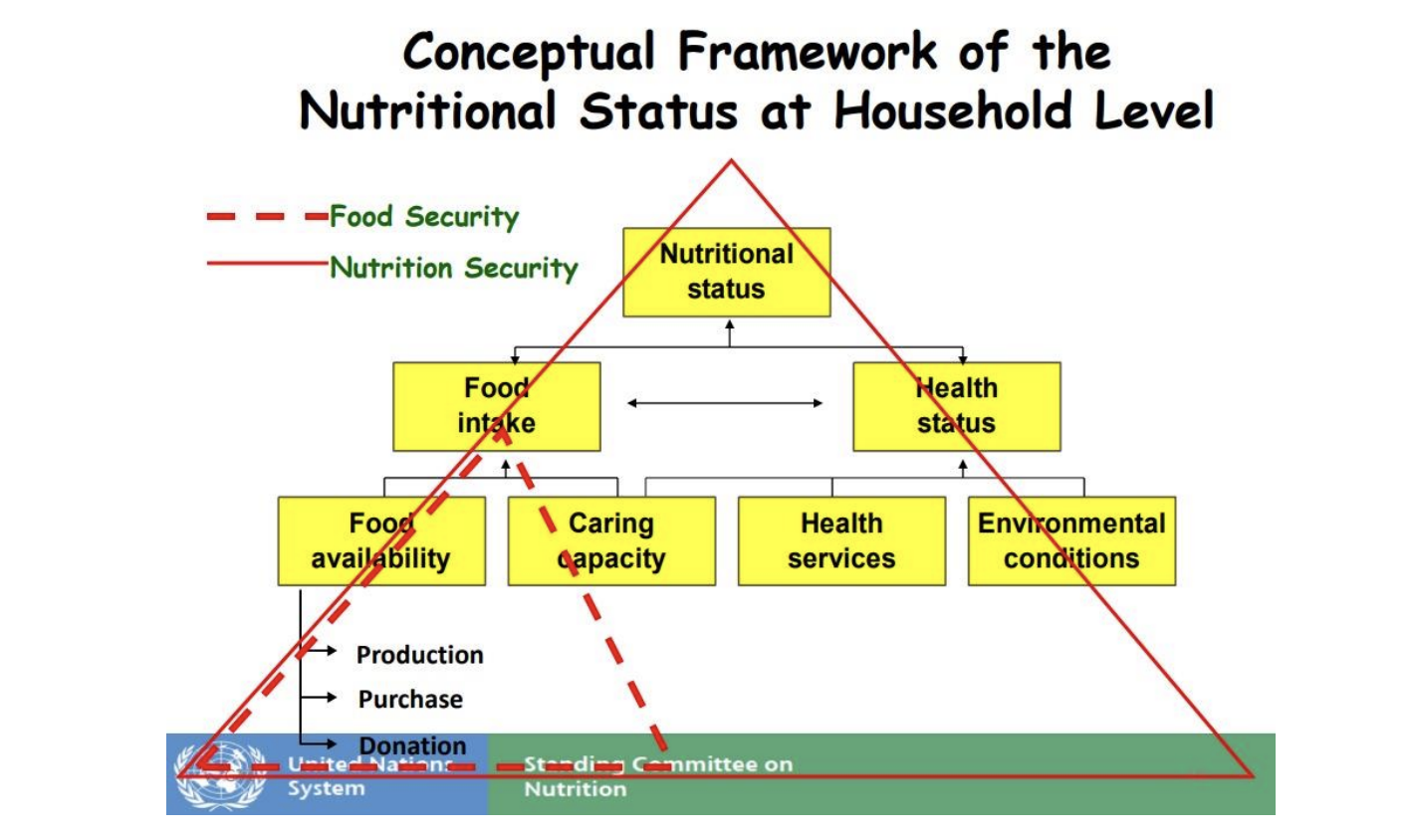
Food and Nutritional security
Food security is when all people at all times have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life. Whereas nutritional security looks into the availability of balanced meals to ensure proper nourishment of the population.
Benefits of proper nutrition
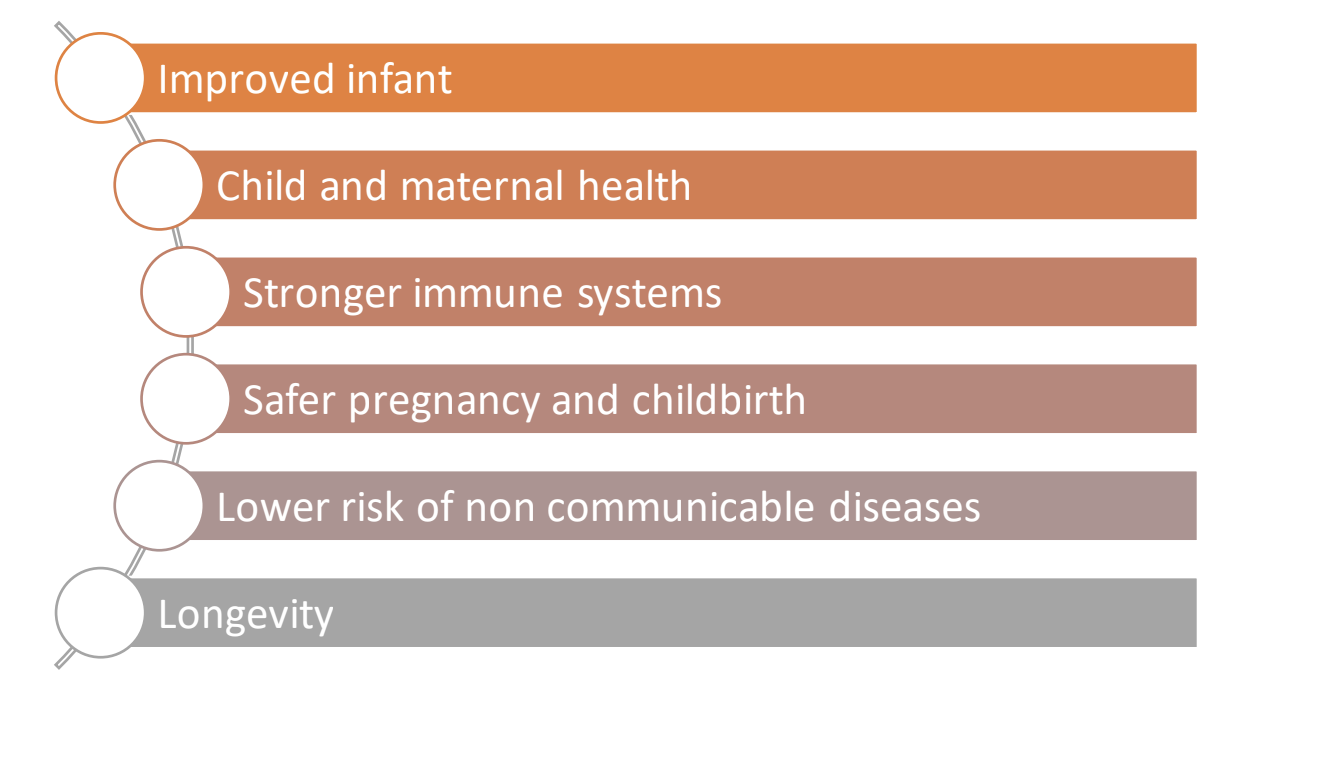
Thus, it is directly or indirectly linked to all SDGs enumerated by the UN.
Malnutrition
- Malnutrition refers to deficiencies, excesses, or imbalances in a person’s intake of energy and/or nutrients. This includes undernutrition, micronutrient related malnutrition, overweight and obesity.
- Women, infants, children, and adolescents are at particular risk of malnutrition.
- Poverty amplifies the risk of malnutrition while malnutrition in turn increases health care costs, reduces productivity, and slows economic growth thereby causing a vicious cycle.
Programmes & Initiatives
Integrated Child Development services
- Launched by Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Umbrella scheme providing initial childhood care for vulnerable groups including children of age 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
National Food Security Act, 2013
- It mandates provision of hot cooked meals for upper primary class children and provides cooking cost for primary and upper primary per child per day to meet the cost of pulses, vegetables, edible oil and condiments.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana
- It constitutes provision of food and essential commodities at subsidized rates for daily needs of the poorest of the poor.
- PM POSHAN
- ‘National Programme for Mid-Day Meal in Schools’ was renamed as Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman
- Launched by Ministry of Education
- It provides one hot cooked meal on all working days to primary and upper primary students in Government and Government-Aided Schools.
PM Matru Vandana Yojana
- Launched in 2017 in coordination with Anganwadi centers, health facilities, Department of Social Welfare & Empowerment and the Department of Health & Family Welfare.
- It is a centrally sponsored direct benefit transfer scheme for pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Under the scheme, Rs. 6,000 is transferred to their bank accounts in three installments.
National Health Mission
- Launched by Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
- Aimed at reinforcing health system in rural and urban areas for reproductive, material, neonatal, child and adolescent health
Anganwadi Services Scheme
- Anganwadi is a centrally sponsored scheme which serves rural child and maternal care.
- It includes supplementary nutrition, pre-school non-formal education, immunization, health check-up, nutrition and health education, and referral services.
Way forward
- Promote awareness on nutrition at household and community level through improved education and accessibility
- Nutrition as holistic idea comprises of health, water, sanitation, gender perspectives, and social norms necessitating development of comprehensive policies
- Lastly, India’s agricultural centres namely villages face the most cases of undernourishment, and thus there is a need to develop mechanism to ensure the nutritional security of villages.
Other NEWS
| Ozone Layer |
|
| People in NEWS | |
| Naik Yeshwant Ghadge |
|
| Baba Mastnath |
|
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs



