Why in NEWS
20th round of corps commander-level talks failed to make any headway to end the LAC stand-off.
The Line of Actual Control (LAC) is a notional demarcation line that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory in the Sino-Indian border dispute. The concept was introduced by Chinese premier Zhou Enlai in a 1959 letter to Jawaharlal Nehru as the “line up to which
each side exercises actual control“, but rejected by Nehru as being incoherent. Subsequently, the term came to refer to the line formed after the 1962 Sino-Indian War.
Classified as 3 sectors
- Western sector: Ladakh and Kashmir
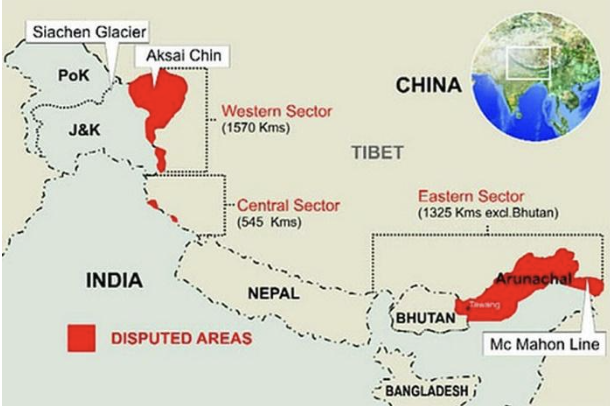
- Middle sector: Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh
- Eastern sector: Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh
The LAC is a strategically important area, as it borders several sensitive regions, including Tibet and Kashmir. It is also home to a number of high-altitude passes and other strategic locations. As a result, both India and China maintain a large military presence along the LAC.
LAC vs LoC

- The LoC emerged from the 1948 ceasefire line negotiated by the UN after the Kashmir War.
- It was designated as the LoC in 1972, following the Shimla Agreement between the two countries (India and Pakistan).
- It is delineated on a map signed by DGMOs of both armies and has the international sanctity of a legal agreement.
On the other hand, the LAC is only a concept. It is not agreed upon by the two countries, neither delineated on a map or demarcated on the ground.
Facts on LAC
- The LAC was established in 1993 as part of a bilateral agreement.
- The Line of Actual Control (LAC) is the unmarked border between India and China.
- It spans across:
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Sikkim
- Uttarakhand
- Jammu & Kashmir.
- It spans across:
- The McMahon Line is the effective boundary between China and India and the line is named after Sir Henry McMahon, exactly between Arunachal Pradesh and Tibet.
- India claims the de facto border is 3,488 kilometers (2,167 miles) long, but China promotes a considerably shorter figure.
Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road initiative was announced by China’s President Xi Jinping in 2013. It was known as the One Belt One Road initiative till 2016 after that it is known as BRI.
Based on the Asian Development Bank (ADB) figures it has been found that Asia faces an infrastructure funding gap of an estimated USD 26 trillion through 2030. So, to address this gap, BRI came up to build better transport connectivity within Asia).
The objectives of the OBOR are as follows
- Creation of a unified large market that makes use of both international and domestic markets.
- Facilitate cultural exchange and integration
- Enhance mutual understanding and trust of member nations that will foster an innovative environment with capital inflows, talent pool and technology database.
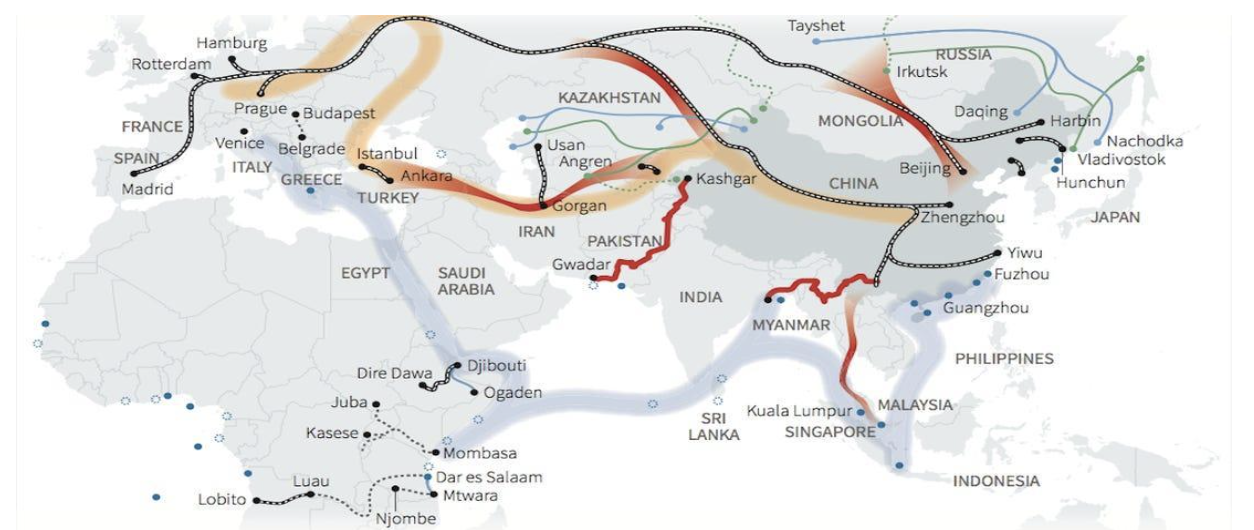
The silk route economic belt
This is a long-term visionary project for the development of infrastructure, connectivity, and economy. In this belt, there are six development corridors present to make connections between different countries. All six corridors are as follows
- New Eurasian Land Bridge Economic Corridor.
- China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor.
- China-Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor.
- China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor.
- Bangladesh-India-China-Myanmar Economic Corridor.
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor.
The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road
It connects China to different South-East Asian countries like India, Indonesia, Somalia, Egypt, and many more. It also connects the South China Sea, Indian Ocean, Gulf of Bengal, and many more.
Some of the core interests of China in the BRI include
- State sovereignty
- National security
- Territorial integrity
- Protection of China’s social stability
- Protection of political system
- Promoting continued economic and social development.
Major Concerns about the OBOR in Asia and Beyond
- Chinese construction companies have a poor track record when operating in foreign nations, chief among them being the mistreatment of local workers.
- The geopolitical aspects of the initiative are that certain nations such as the United Nations and Russia view it as a risk to their influence in their respective regions.
- The ultimate risk is of falling into a ‘debt trap’. The exorbitant funding for unsound projects to secure Chinese access to local resources, instead of helping the local economy will leave such nations vulnerable to Chinese influence.
- Countries who have been part of the OBOR have accused China of practising credit imperialism by charging exorbitant rates of interest.
India’s Stand on the OBOR Initiative
- Delhi’s strategic community has long objected to China’s road construction on land frontiers and port-building in the Indian Ocean as “strategic encirclement”.
- The problem is even more compounded with the presence of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- Canning the issue will be paving the way for India’s marginalisation from the unfolding geo-economic Options for India
Potential Advantages to India
- that will help India’s border and outlying areas to develop the infrastructure that it presently lacks.
- Funds from financial institutions may be more easily available and support from China and its infrastructure construction companies may also then be readily available.
- This project will help improve connectivity with India’s neighbors improving the economic, diplomatic, and strategic relationship.
Other NEWS
| Operation Ajay |
|
| Space Economy in India |
|
| Ninjacart |
|
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs



