About: Tuberculosis is a dangerous infectious disease that spreads easily and usually affects the lungs.
Cause: Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacteria that causes tuberculosis.
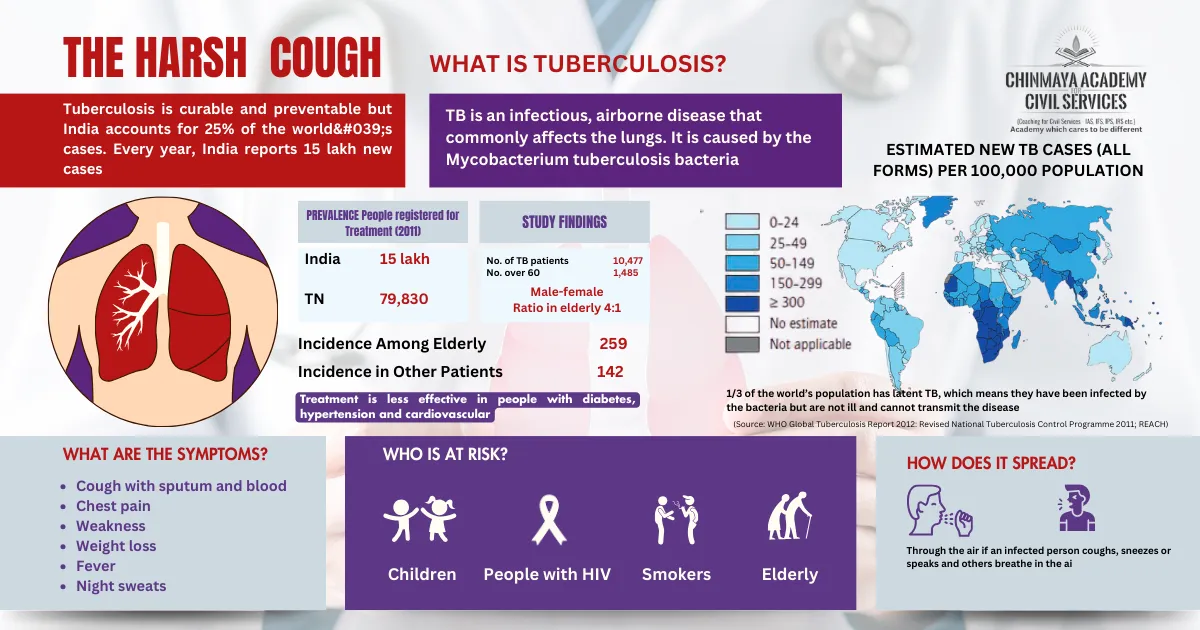
Transmission: if a person with tuberculosis (TB) of the lungs or throat coughs, speaks, or sings, the bacteria can enter the air and spread to other people.
Symptom
- Pain in the chest
- Coughing up blood and sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs weakness or fatigue
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Chills and fever
- Sweating at night
Medication – Ethambutol (HRZE), Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, and Isoniazid (INH) are taken daily.
Types of TB
Pulmonary TB
- The most contagious form of tuberculosis is pulmonary TB, which typically only spreads after a person has been exposed to the illness for an extended period of time.
- The immune system, the body’s natural defense against disease and infection, eliminates the bacteria in the majority of healthy individuals, leaving them symptomless.
Latent TB
- In certain cases, the immune system stops the bacteria from spreading throughout the body but is unable to eradicate it.
- The bacteria will still be present in your body, but you won’t experience any symptoms.
- Individuals who have latent tuberculosis are not contagious.
Active TB
- If the immune system fails to kill or contain the infection, it can spread to the lungs or other parts of the body, causing symptoms within a few weeks or months. This is known as active tuberculosis.
- It is estimated that one-quarter of the world’s population is infected with tuberculosis bacteria, but only 5-15% will develop active tuberculosis.
- Latent tuberculosis (TB) can progress to active tuberculosis at a later stage, especially if your immune system weakens.
India’s Initiative
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana (NPY) – Nutritional Support to tuberculosis – Assists in providing TB patients with the nutrition they need, particularly the underprivileged
- By 2025, the National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP) seeks to systematically lower India’s TB burden.
- The National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination was established with the mission of achieving the goal of eliminating tuberculosis by 2025.
- The Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan aims to bring together all community stakeholders to support those receiving TB treatment and accelerate the country’s progress towards TB elimination Bedaquiline and Delamanid made available at an reduced price
- Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centers aims to decentralise comprehensive primary healthcare, including tuberculosis care, at the grassroots level.
Global Initiative
- End TB Strategy by World Health Organization (WHO)
- It provides a roadmap for countries to reduce tuberculosis incidence by 80%, TB deaths by 90%, and eliminate catastrophic costs for TB-affected households by 2030.
- World Development Report (1993), published by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- According to the report, adult tuberculosis treatment is the best buy among all developmental interventions.
- The Global Fund – A global movement to eliminate HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria and ensure a healthier, safer, and more equitable future for all.
- The Stop TB Partnership brings together expertise from a broad spectrum of country, regional, and global partners in our shared mission of revolutionising the TB space and ending TB by 2030.
- Sustainable Development Goal 3 – To end the tuberculosis epidemic by 2030
Challenges in eradication of Tuberculosis
- Rural areas have poor primary healthcare infrastructure.
- Unregulated private health care results in widespread irrational use of first- and second-line anti-TB drugs.
- Unpasteurized milk or dairy products made from raw milk is another possible source of tuberculosis in humans.
- Definitions of ‘end’ tuberculosis is not clear.
- Lack of awareness
- Multi Drug Resistant TB
Multi Drug Resistant TB
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB), can develop resistance to the antibiotics used to treat the disease.
- MDR-TB is defined as TB that does not respond to at least one of the two most powerful anti-TB drugs, isoniazid or rifampicin.
- The majority of tuberculosis patients are cured by following to a strict 6-month treatment plan that is provided with support and supervision.
- Inappropriate or incorrect use of antimicrobial drugs, or the use of ineffective drug formulations (such as single drugs, poor quality medicines, or poor storage conditions), as well as premature treatment interruption, can lead to drug resistance, which can then be transmitted, particularly in crowded settings such as prisons and hospitals.
- Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is a rare form of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) that is resistant to isoniazid, rifampin, any fluoroquinolone, and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). It was reported in 1117 countries worldwide.
More read
 Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs Chinmaya IAS Academy – Current Affairs
